A company is setting up products to deploy in AWS Service Catalog. Management is concerned that when users launch products, elevated IAM privileges will be required to create resources.
How should the company mitigate this concern?
B
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/mt/how-to-launch-secure-and-governed-aws-resources-with-aws-cloudformation-and-aws-service-catalog/
A company is implementing a new application in a new AWS account. A VPC and subnets have been created for the application. The application has been peered to an existing VPC in another account in the same AWS Region for database access. Amazon EC2 instances will regularly be created and terminated in the application VPC, but only some of them will need access to the databases in the peered VPC over TCP port 1521. A security engineer must ensure that only the
EC2 instances than need access to the databases can access them through the network.
How can the security engineer implement this solution?
A
A company is running an application on Amazon EC2 instances in an Auto Scaling group. The application stores logs locally. A security engineer noticed that logs were lost after a scale-in event. The security engineer needs to recommend a solution to ensure the durability and availability of log data. All logs must be kept for a minimum of 1 year for auditing purposes.
What should the security engineer recommend?
A
A company needs to retain log data archives for several years to be compliant with regulations. The log data is no longer used, but it must be retained.
What is the MOST secure and cost-effective solution to meet these requirements?
C
A company uses an Amazon S3 bucket to store reports. Management has mandated that all new objects stored in this bucket must be encrypted at rest using server-side encryption with a client specified AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) CMK owned by the same account as the S3 bucket. The AWS account number is 111122223333, and the bucket name is reportbucket. The company's security specialist must write the S3 bucket policy to ensure the mandate can be implemented.
Which statement should the security specialist include in the policy?
A.
B.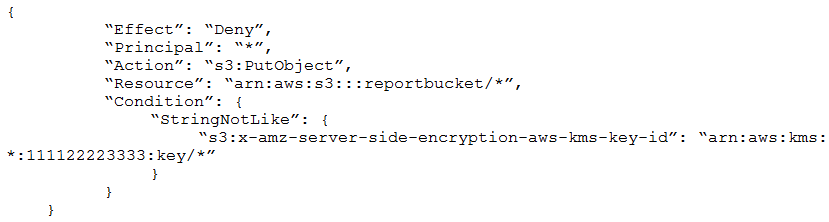
C.
D.
A
A company website runs on Amazon EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB). The instances run in an Auto Scaling group across multiple
Availability Zones. There is an Amazon CloudFront distribution in front of the ALB. Users are reporting performance problems. A security engineer discovers that the website is receiving a high rate of unwanted requests to the CloudFront distribution originating from a series of source IP addresses.
How should the security engineer address this problem?
D
A developer is building a serverless application hosted on AWS that uses Amazon Redshift as a data store. The application has separate module for read/write and read-only functionality. The modules need their own database users for compliance reasons.
Which combination of steps should a security engineer implement to grant appropriate access? (Choose two.)
AD
A company uses an external identity provider to allow federation into different AWS accounts. A security engineer for the company needs to identify the federated user that terminated a production Amazon EC2 instance a week ago.
What is the FASTEST way for the security engineer to identify the federated user?
A
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/how-to-easily-identify-your-federated-users-by-using-aws-cloudtrail/
A company has two software development teams that are creating applications that store sensitive data in Amazon S3. Each team's data must always be separate. The company's security team must design a data encryption strategy for both teams that provides the ability to audit key usage. The solution must also minimize operational overhead.
What should the security team recommend?
B
A security engineer is designing a solution that will provide end-to-end encryption between clients and Docker containers running in Amazon Elastic Container
Service (Amazon ECS). This solution will also handle volatile traffic patterns.
Which solution would have the MOST scalability and LOWEST latency?
B