You receive numerous alerts from Azure Monitor for an Azure SQL Database instance.
You need to reduce the number of alerts. You must only receive alerts if there is a significant change in usage patterns for an extended period.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Answer:
BD
B: Dynamic Thresholds continuously learns the data of the metric series and tries to model it using a set of algorithms and methods. It detects patterns in the data such as seasonality (Hourly / Daily / Weekly), and is able to handle noisy metrics (such as machine CPU or memory) as well as metrics with low dispersion (such as availability and error rate).
D: Alert threshold sensitivity is a high-level concept that controls the amount of deviation from metric behavior required to trigger an alert.
Low ג€" The thresholds will be loose with more distance from metric series pattern. An alert rule will only trigger on large deviations, resulting in fewer alerts.
Incorrect Answers:
A: High ג€" The thresholds will be tight and close to the metric series pattern. An alert rule will be triggered on the smallest deviation, resulting in more alerts.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-monitor/platform/alerts-dynamic-thresholds
HOTSPOT -
You have an on-premises Microsoft SQL Server 2016 server named Server1 that contains a database named DB1.
You need to perform an online migration of DB1 to an Azure SQL Database managed instance by using Azure Database Migration Service.
How should you configure the backup of DB1? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: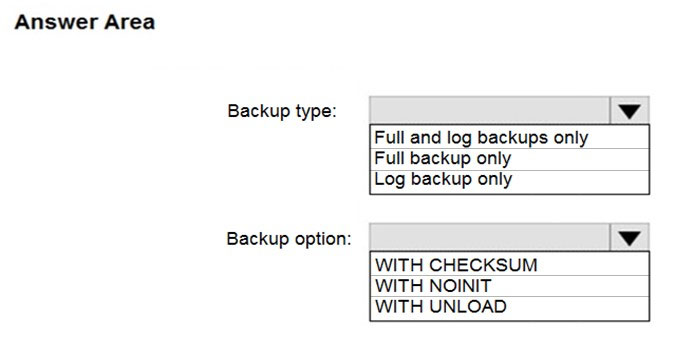
Answer:
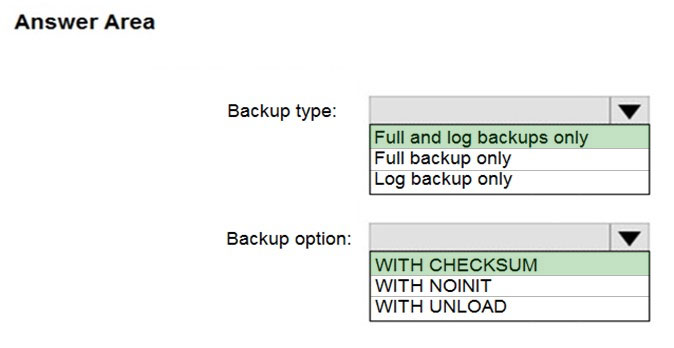
Box 1: Full and log backups only
Make sure to take every backup on a separate backup media (backup files). Azure Database Migration Service doesn't support backups that are appended to a single backup file. Take full backup and log backups to separate backup files.
Box 2: WITH CHECKSUM -
Azure Database Migration Service uses the backup and restore method to migrate your on-premises databases to SQL Managed Instance. Azure Database
Migration Service only supports backups created using checksum.
Incorrect Answers:
NOINIT Indicates that the backup set is appended to the specified media set, preserving existing backup sets. If a media password is defined for the media set, the password must be supplied. NOINIT is the default.
UNLOAD -
Specifies that the tape is automatically rewound and unloaded when the backup is finished. UNLOAD is the default when a session begins.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/dms/known-issues-azure-sql-db-managed-instance-online
DRAG DROP -
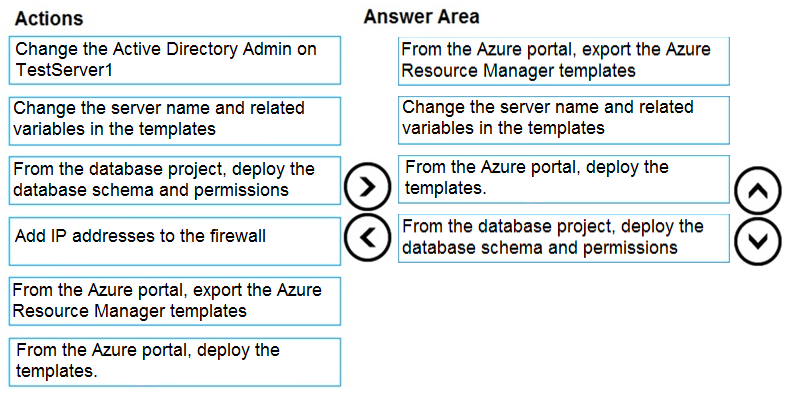
You have a resource group named App1Dev that contains an Azure SQL Database server named DevServer1. DevServer1 contains an Azure SQL database named DB1. The schema and permissions for DB1 are saved in a Microsoft SQL Server Data Tools (SSDT) database project.
You need to populate a new resource group named App1Test with the DB1 database and an Azure SQL Server named TestServer1. The resources in App1Test must have the same configurations as the resources in App1Dev.
Which four actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:
Answer:
HOTSPOT -
You have an Azure Synapse Analytics dedicated SQL pool named Pool1 and an Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account named Account1.
You plan to access the files in Account1 by using an external table.
You need to create a data source in Pool1 that you can reference when you create the external table.
How should you complete the Transact-SQL statement? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: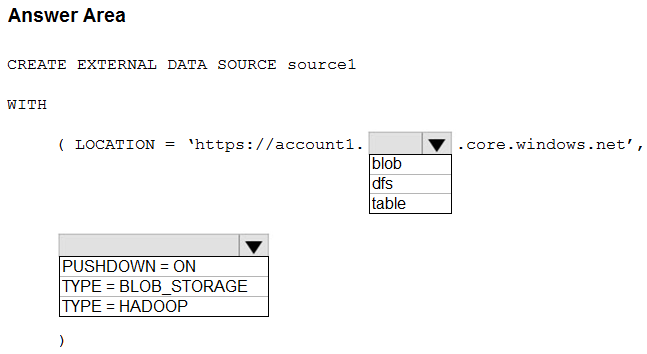
Answer:
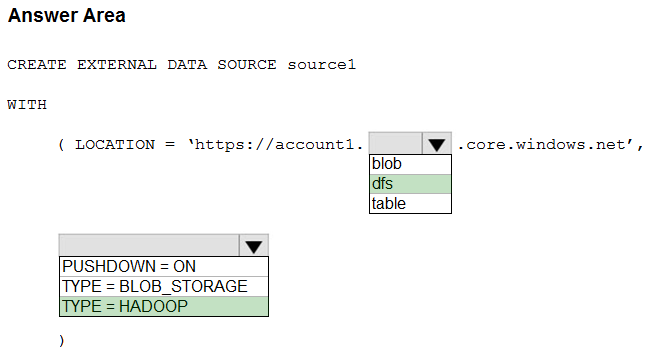
Box 1: dfs -
For Azure Data Lake Store Gen 2 used the following syntax:
http[s] <storage_account>.dfs.core.windows.net/<container>/subfolders
Incorrect:
Not blob: blob is used for Azure Blob Storage. Syntax:
http[s] <storage_account>.blob.core.windows.net/<container>/subfolders
Box 2: TYPE = HADOOP -
Syntax for CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE.
External data sources with TYPE=HADOOP are available only in dedicated SQL pools.
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE <data_source_name>
WITH -
( LOCATION = '<prefix>://<path>'
[, CREDENTIAL = <database scoped credential> ]
, TYPE = HADOOP
)
[;]
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/synapse-analytics/sql/develop-tables-external-tables
HOTSPOT -
You plan to develop a dataset named Purchases by using Azure Databricks. Purchases will contain the following columns:
✑ ProductID
✑ ItemPrice
✑ LineTotal
✑ Quantity
✑ StoreID
✑ Minute
✑ Month
✑ Hour
✑ Year
✑ Day
You need to store the data to support hourly incremental load pipelines that will vary for each StoreID. The solution must minimize storage costs.
How should you complete the code? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: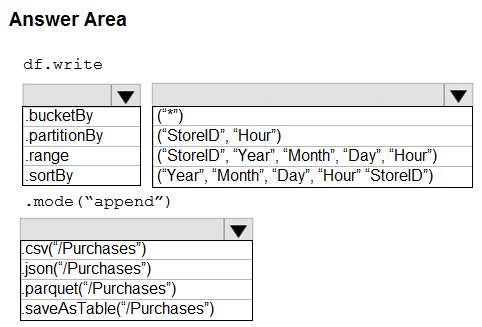
Answer:
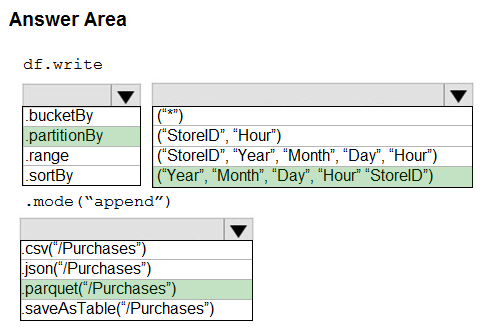
Box 1: .partitionBy -
Example:
df.write.partitionBy("y","m","d")
.mode(SaveMode.Append)
.parquet("/data/hive/warehouse/db_name.db/" + tableName)
Box 2: ("Year","Month","Day","Hour","StoreID")
Box 3: .parquet("/Purchases")
Reference:
https://intellipaat.com/community/11744/how-to-partition-and-write-dataframe-in-spark-without-deleting-partitions-with-no-new-data
You are designing a streaming data solution that will ingest variable volumes of data.
You need to ensure that you can change the partition count after creation.
Which service should you use to ingest the data?
Answer:
D
The partition count for an event hub in a dedicated Event Hubs cluster can be increased after the event hub has been created.
Incorrect Answers:
A: For Azure Event standard hubs, the partition count isn't changeable, so you should consider long-term scale when setting partition count.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/event-hubs/event-hubs-features#partitions
You have an Azure SQL database named sqldb1.
You need to minimize the amount of space by the data and log files of sqldb1.
What should you run?
Answer:
A
DBCC SHRINKDATABASE shrinks the size of the data and log files in the specified database.
Incorrect Answers:
D: To shrink one data or log file at a time for a specific database, execute the DBCC SHRINKFILE command.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/t-sql/database-console-commands/dbcc-shrinkdatabase-transact-sql
You have an Azure SQL Database server named sqlsrv1 that hosts 10 Azure SQL databases.
The databases perform slower than expected.
You need to identify whether the performance issue relates to the use of tempdb by Azure SQL databases in sqlsrv1.
What should you do?
Answer:
D
Microsoft Azure SQL Database and Azure SQL Managed Instance enable a subset of dynamic management views to diagnose performance problems, which might be caused by blocked or long-running queries, resource bottlenecks, poor query plans, and so on.
This include edentifying tempdb performance issues:
When identifying IO performance issues, the top wait types associated with tempdb issues is PAGELATCH_* (not PAGEIOLATCH_*).
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-sql/database/monitoring-with-dmvs
You have an Azure Data Factory pipeline that is triggered hourly.
The pipeline has had 100% success for the past seven days.
The pipeline execution fails, and two retries that occur 15 minutes apart also fail. The third failure returns the following error.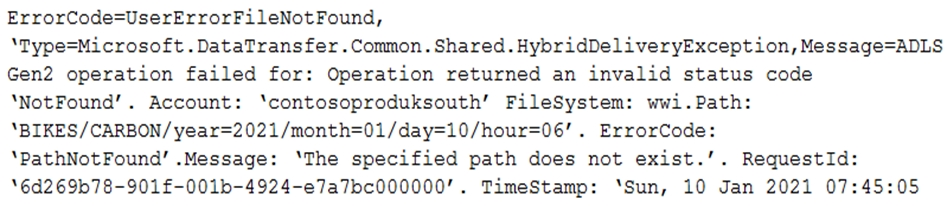
What is a possible cause of the error?
Answer:
B
A file is missing.
Incorrect:
Not A, not C, not D: Time of the error is 07:45.
HOTSPOT -
You have an Azure SQL database.
You are reviewing a slow performing query as shown in the following exhibit.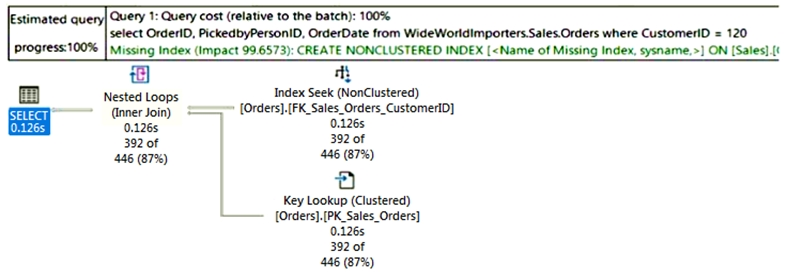
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Answer:

Box 1: Live Query Statistics -
Live Query Statistics as it a percentage of the execution.
Box 2: Key Lookup -
The use of a Key Lookup operator in a query plan indicates that the query might benefit from performance tuning. For example, query performance might be improved by adding a covering index.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/performance/live-query-statistics?view=sql-server-ver15 https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sql/relational-databases/showplan-logical-and-physical-operators-reference