You are deploying an Azure IoT Edge solution that includes multiple IoT Edge devices.
You need to configure module-to-module routing.
To which section of the deployment manifest should you add the routes?
B
Routes are declared in the $edgeHub desired properties.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-edge/module-composition
You have an IoT device that has the following configurations:
✑ Hardware: Raspberry Pi
✑ Operating system: Raspbian
You need to deploy Azure IoT Edge to the device.
Which two actions should you perform? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
AB
The Azure IoT Edge runtime is what turns a device into an IoT Edge device. The runtime can be deployed on devices as small as a Raspberry Pi or as large as an industrial server.
The IoT Edge security daemon provides and maintains security standards on the IoT Edge device. The daemon starts on every boot and bootstraps the device by starting the rest of the IoT Edge runtime.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-edge/how-to-install-iot-edge
You develop a custom Azure IoT Edge module named temperature-module.
You publish temperature-module to a private container registry named mycr.azurecr.io
You need to build a deployment manifest for the IoT Edge device that will run temperature-module.
Which three container images should you define in the manifest? Each correct answer presents part of the solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
BDE
Each IoT Edge device runs at least two modules: $edgeAgent and $edgeHub, which are part of the IoT Edge runtime. IoT Edge device can run multiple additional modules for any number of processes. Use a deployment manifest to tell your device which modules to install and how to configure them to work together.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-edge/module-composition
DRAG DROP -
You need to install the Azure IoT Edge runtime on a new device that runs Windows 10 IoT Enterprise.
Which four actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place: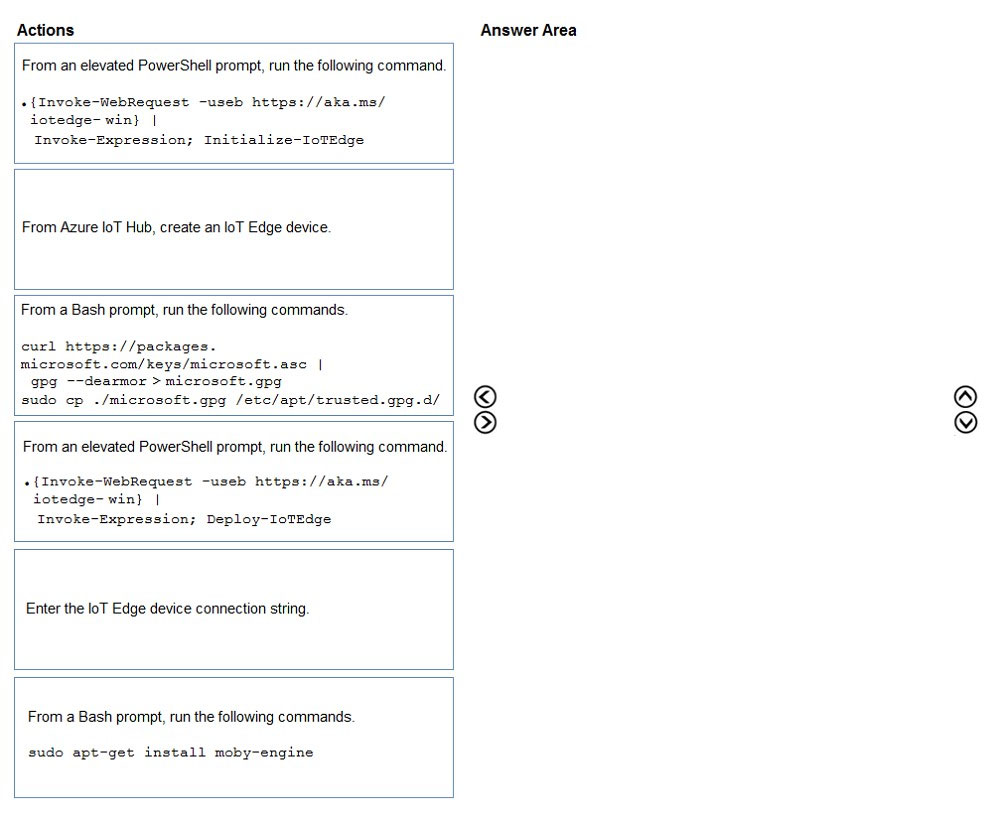
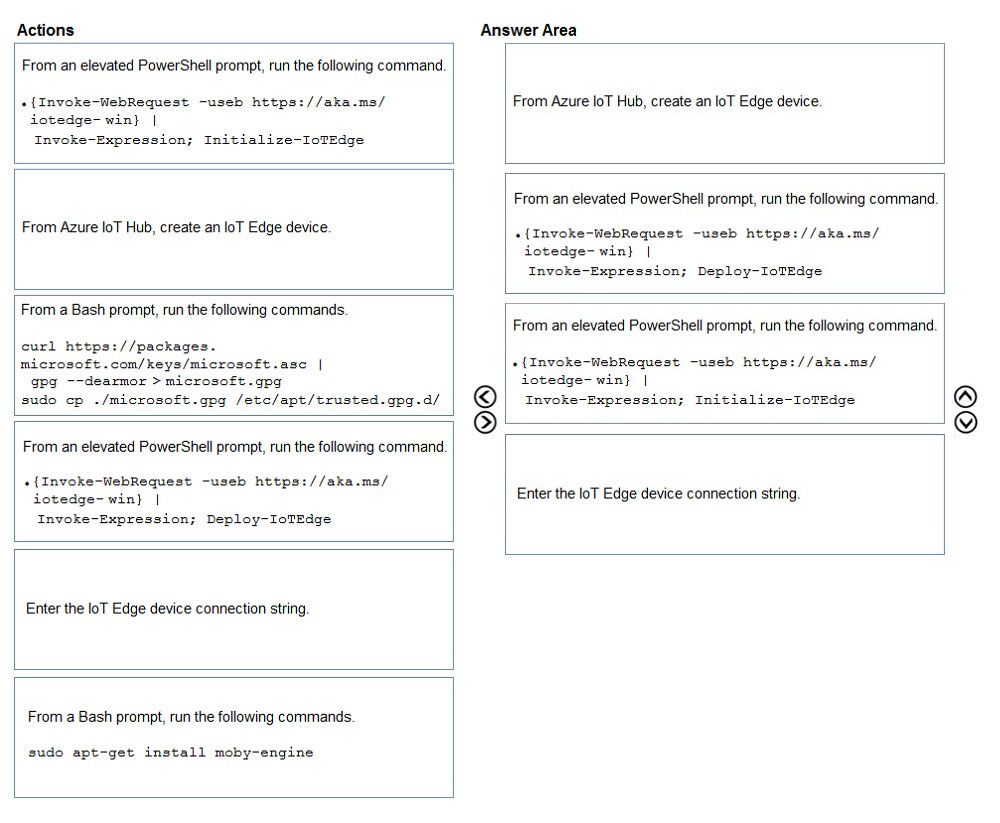
Step 1: From Azure IoT Hub, create an IoT Edge Device
Step 2: Deploy-IoTEdge -
The Deploy-IoTEdge command checks that your Windows machine is on a supported version, turns on the containers feature, and then downloads the moby runtime and the IoT Edge runtime. The command defaults to using Windows containers.
{Invoke-WebRequest -useb https://aka.ms/iotedge-win} | Invoke-Expression; `
Deploy-IoTEdge -
Step 3: Initialize-IoTEdge -
The Initialize-IoTEdge command configures the IoT Edge runtime on your machine. The command defaults to manual provisioning with Windows containers.
{Invoke-WebRequest -useb https://aka.ms/iotedge
Step 4: Enter the IoT Edge device connection string.
When prompted, provide the device connection string that you retrieved in step 1. The device connection string associates the physical device with a device ID in
IoT Hub.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-edge/module-composition
You have an Azure IoT solution that includes an Azure IoT Hub named Hub1 and an Azure IoT Edge device named Edge1. Edge1 connects to Hub1.
You need to deploy a temperature module to Edge1.
What should you do?
D
You deploy modules to your device by applying the deployment manifest that you configured with the module information.
Change directories into the folder where your deployment manifest is saved. If you used one of the VS Code IoT Edge templates, use the deployment.json file in the config folder of your solution directory and not the deployment.template.json file.
Use the following command to apply the configuration to an IoT Edge device: az iot edge set-modules --device-id [device id] --hub-name [hub name] --content [file path]
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-edge/how-to-deploy-modules-cli
DRAG DROP -
Your company is creating a new camera security system that will use Azure IoT Hub.
You plan to use an Azure IoT Edge device that will run Ubuntu Server 18.04.
You need to configure the IoT Edge device.
Which three actions should you perform in sequence? To answer, move the appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
Select and Place:

Step1: Install the IoT edge repository for Ubuntu Server 18.04 on the physical device. From IoT hub, create a new IoT Edge device.
Prepare your device to access the Microsoft installation packages.
Install the repository configuration that matches your device operating system.
Ubuntu Server 18.04: curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/18.04/multiarch/prod.list > ./microsoft-prod.list
In your IoT Hub in the Azure portal, IoT Edge devices are created and managed separately from IOT devices that are not edge enabled.
1. Sign in to the Azure portal and navigate to your IoT hub.
2. In the left pane, select IoT Edge from the menu.
3. Select Add an IoT Edge device.
4. Provide a descriptive device ID. Use the default settings to auto-generate authentication keys and connect the new device to your hub.
5. Select Save.
Step 2: Run the following commandsג€¦
Install the container runtime.
Azure IoT Edge relies on an OCI-compatible container runtime. For production scenarios, we recommended that you use the Moby-based engine provided below.
The Moby engine is the only container engine officially supported with Azure IoT Edge. Docker CE/EE container images are compatible with the Moby runtime.
Install the Moby engine.
sudo apt-get install moby-engine
Install the Moby command-line interface (CLI). The CLI is useful for development but optional for production deployments. sudo apt-get install moby-cli
Install the security daemon. The package is installed at /etc/iotedge/. sudo apt-get install iotedge
Step 3: Add the connection string to the /etc/iotedge/config.yaml file,..
To manually provision a device, you need to provide it with a device connection string that you can create by registering a new device in your IoT hub.
Open the configuration file.
sudo nano /etc/iotedge/config.yaml
Find the provisioning configurations of the file and uncomment the Manual provisioning configuration section. Update the value of device_connection_string with the connection string from your IoT Edge device.
Save and close the file.
After entering the provisioning information in the configuration file, restart the daemon: sudo systemctl restart iotedge
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-edge/how-to-install-iot-edge-linux
You have the devices shown in the following table.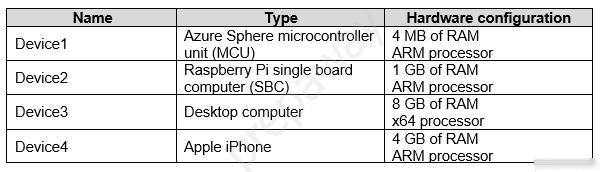
You are implementing a proof of concept (POC) for an Azure IoT solution.
You need to deploy an Azure IoT Edge device as part of the POC.
On which two devices can you deploy IoT Edge? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
BC
Azure IoT Edge runs great on devices as small as a Raspberry Pi3 to server grade hardware.
Tier 1.
The systems listed in the following table are supported by Microsoft, either generally available or in public preview, and are tested with each new release.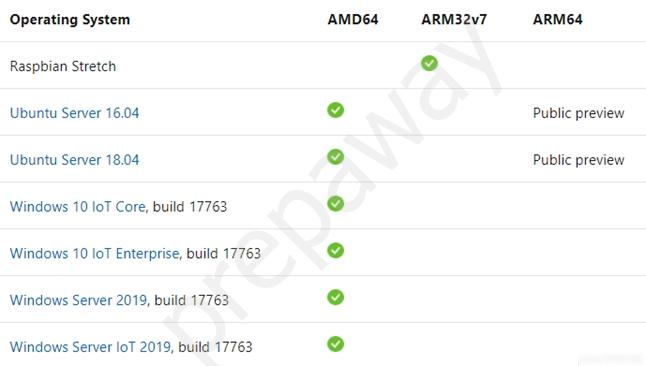
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-edge/support
HOTSPOT -
You need to configure Azure IoT Edge module routing to ensure that modules route traffic as shown in the following exhibit.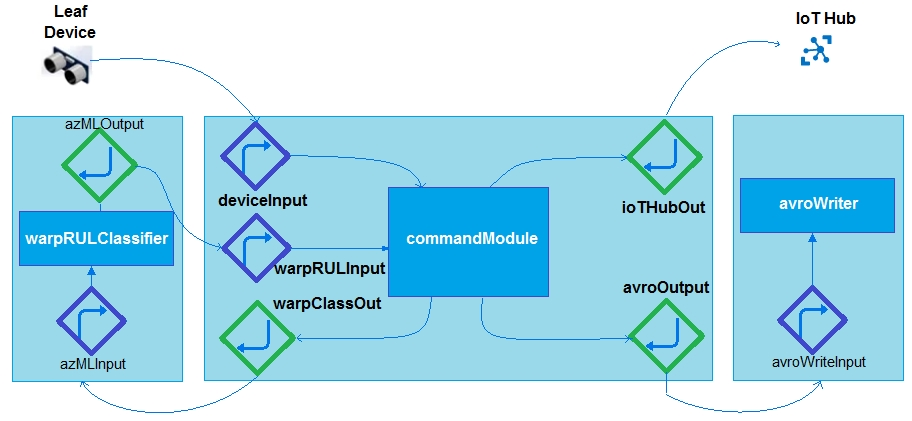
How should you complete the IoT Edge module routes? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:

Box 1: $connectionModuled -
Add a route that tells the edge hub to route any message received by the IoT Edge device that was not sent by an IoT Edge module.
Box 2: $upstream -
Send messages to $upstream, which passes the messages to the connected IoT Hub.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-edge/tutorial-machine-learning-edge-06-custom-modules
DRAG DROP -
You have an Azure IoT Edge device named Edge1.
You need to configure the module container to link the module storage to the host storage.
How should you configure the deployment manifest? To answer, drag the appropriate keys to the correct targets. Each key may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place: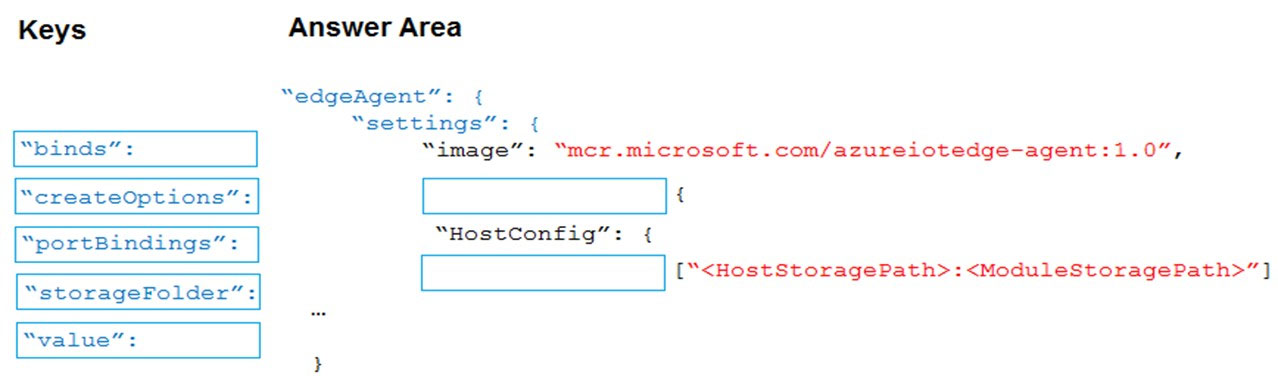
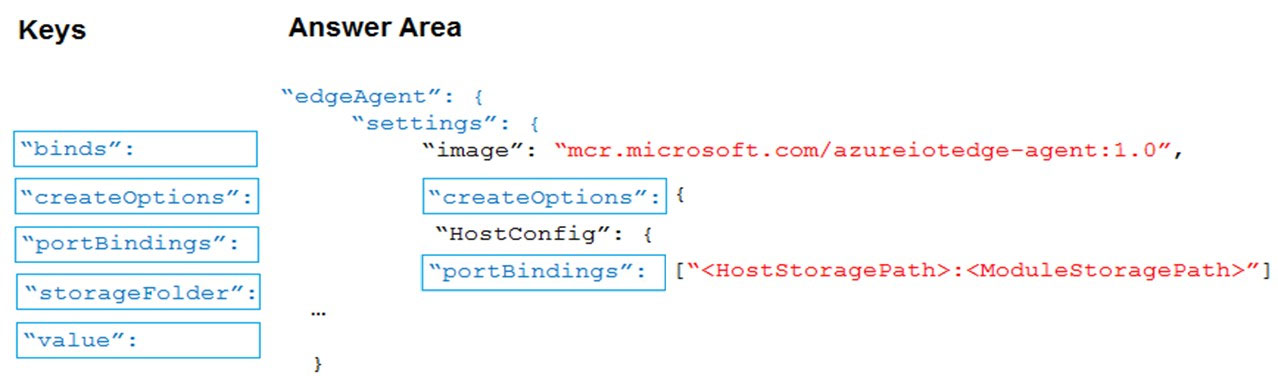
Box 1: createOptions -
Every module has a settings property that contains the module image, an address for the container image in a container registry, and any createOptions to configure the image on startup.
Box 2: portbindings -
Use the PortBindings setting in the HostConfig group of the Docker container create options to map the exposed port in the module to a port on the host device.
For example, if you exposed port 8080 inside the module and want to map that to port 80 of the host device, the create options in the template.json file would look like the following example:
"createOptions": {
"HostConfig": {
"PortBindings": {
"8080/tcp": [
{
"HostPort": "80"
}
]
}
}
}
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-edge/how-to-use-create-options
You are developing an Azure IoT solution for a shipping company. The company's ships will have sensors used for predictive maintenance. Some sensor devices will be MQTT-capable, and others will use Modbus.
Each ship has an internet connection that is available only when the ship is docked.
You create an Azure IoT hub.
You need to implement an IoT solution that uses Azure IoT Edge.
What should you do?
C
Note: If you want to connect IoT devices that use Modbus TCP or RTU protocols to an Azure IoT hub, you can use an IoT Edge device as a gateway. The gateway device reads data from your Modbus devices, then communicates that data to the cloud using a supported protocol.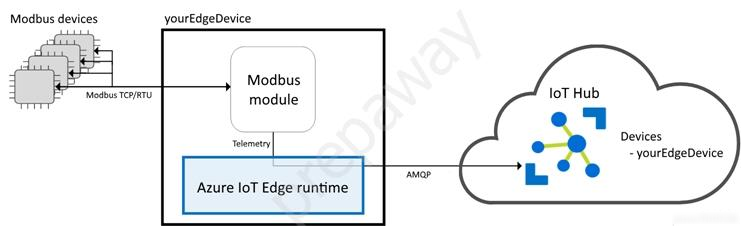
Incorrect Answers:
A: The MQTT devices should be added to the IoT hub.
B: Need to use an IoT Edge Modbus module.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/iot-edge/deploy-modbus-gateway