When configuring IPv6 on an interface, which two IPv6 multicast groups are joined? (Choose two.)
DE
When an interface is configured with IPv6 address, it automatically joins the all nodes (FF02::1) and solicited-node (FF02::1:FFxx:xxxx) multicast groups. The all- node group is used to communicate with all interfaces on the local link, and the solicited-nodes multicast group is required for link-layer address resolution.
Routers also join a third multicast group, the all-routers group (FF02::2).
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/ipv6/configuration/xe-3s/ipv6-xe-36s-book/ip6-multicast.html
DRAG DROP -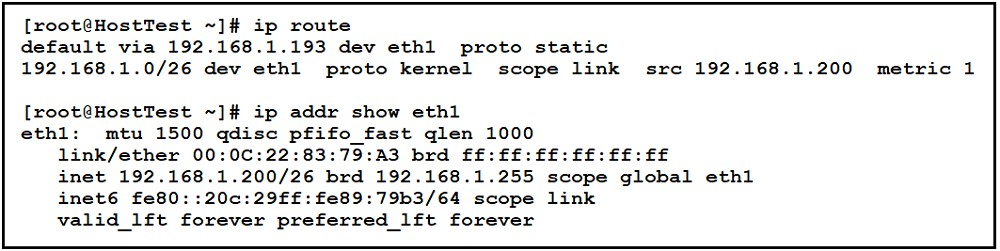
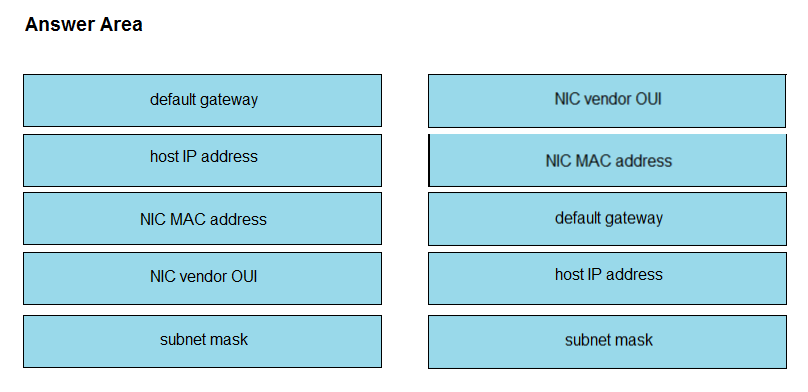
Refer to the exhibit. Drag and drop the networking parameters from the left onto the correct values on the right.
Select and Place:
The ג€ip routeג€ and ג€ip addr show eth1ג€ are Linux commands.
ג€¢ ג€ip routeג€: display the routing table
ג€¢ ג€ip addr show eth1ג€: get depth information (only on eth1 interface) about your network interfaces like IP Address, MAC Address information
What is the default behavior of a Layer 2 switch when a frame with an unknown destination MAC address is received?
C
If the destination MAC address is not in the CAM table (unknown destination MAC address), the switch sends the frame out all other ports that are in the same
VLAN as the received frame. This is called flooding. It does not flood the frame out the same port on which the frame was received.
An engineer must configure a /30 subnet between two routes. Which usable IP address and subnet mask combination meets this criteria?
D
Which network allows devices to communicate without the need to access the Internet?
B
This question asks about the private ranges of IPv4 addresses. The private ranges of each class of IPv4 are listed below:
Class A private IP address ranges from 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
Class B private IP address ranges from 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
Class C private IP address ranges from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
Only the network 172.28.0.0/16 belongs to the private IP address (of class B).

Refer to the exhibit. Which statement explains the configuration error message that is received?
D
Which IPv6 address type provides communication between subnets and cannot route on the Internet?
B
A IPv6 Unique Local Address is an IPv6 address in the block FC00::/7. It is the approximate IPv6 counterpart of the IPv4 private address. It is not routable on the global Internet.
Note: In the past, Site-local addresses (FEC0::/10) are equivalent to private IP addresses in IPv4 but now they are deprecated.
Link-local addresses only used for communications within the local subnet. It is usually created dynamically using a link-local prefix of FE80::/10 and a 64-bit interface identifier (based on 48-bit MAC address).
Which IPv6 address block sends packets to a group address rather than a single address?
D
FF00::/8 is used for IPv6 multicast and this is the IPv6 type of address the question wants to ask.
FE80::/10 range is used for link-local addresses. Link-local addresses only used for communications within the local subnetwork (automatic address configuration, neighbor discovery, router discovery, and by many routing protocols). It is only valid on the current subnet. It is usually created dynamically using a link-local prefix of FE80::/10 and a 64-bit interface identifier (based on 48-bit MAC address).
What are two reasons that cause late collisions to increment on an Ethernet interface? (Choose two.)
BE
A late collision is defined as any collision that occurs after the first 512 bits (or 64th byte) of the frame have been transmitted. The usual possible causes are full- duplex/half-duplex mismatch, exceeded Ethernet cable length limits, or defective hardware such as incorrect cabling, non-compliant number of hubs in the network, or a bad NIC.
Late collisions should never occur in a properly designed Ethernet network. They usually occur when Ethernet cables are too long or when there are too many repeaters in the network.
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/internetworking/troubleshooting/guide/tr1904.html
What is a benefit of using a Cisco Wireless LAN Controller?
A