A Developer is creating an AWS Lambda function that requires environment variables to store connection information and logging settings. The Developer is required to use an AWS KMS Customer Master Key (CMK) supplied by the Information Security department in order to adhere to company standards for securing
Lambda environment variables.
Which of the following are required for this configuration to work? (Choose two.)
DE
A Developer signed in to a new account within an AWS Organizations organizational unit (OU) containing multiple accounts. Access to the Amazon S3 service is restricted with the following SCP:
How can the Security Engineer provide the Developer with Amazon S3 access without affecting other accounts?
C
A company has several workloads running on AWS. Employees are required to authenticate using on-premises ADFS and SSO to access the AWS Management
Console. Developers migrated an existing legacy web application to an Amazon EC2 instance. Employees need to access this application from anywhere on the internet, but currently, there is no authentication system built into the application.
How should the Security Engineer implement employee-only access to this system without changing the application?
C
An Application Developer is using an AWS Lambda function that must use AWS KMS to perform encrypt and decrypt operations for API keys that are less than 2
KB.
Which key policy would allow the application to do this while granting least privilege?
A.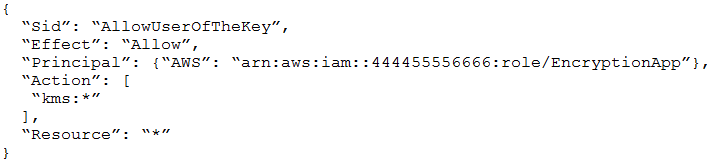
B.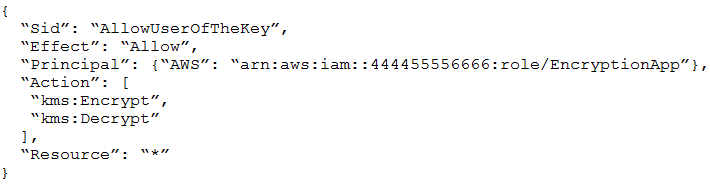
C.
D.
C
A company is migrating its legacy workloads to AWS. The current security information events management (SIEM) system that analyzes logs is aging, and different SIEM systems are being evaluated to replace it. The company wants to change SIEMs without re-architecture the solution.
What should the Security Engineer do to accomplish this with minimal operational impact?
B
An Application team has requested a new AWS KMS master key for use with Amazon S3, but the organizational security policy requires separate master keys for different AWS services to limit blast radius.
How can an AWS KMS customer master key (CMK) be constrained to work with only Amazon S3?
B
Reference:
https://www.slideshare.net/AmazonWebServices/protecting-your-data-with-aws-kms-and-aws-cloudhsm
(17)
A company is developing a highly resilient application to be hosted on multiple Amazon EC2 instances. The application will store highly sensitive user data in
Amazon RDS tables.
The application must:
✑ Include migration to a different AWS Region in the application disaster recovery plan.
✑ Provide a full audit trail of encryption key administration events.
✑ Allow only company administrators to administer keys.
✑ Protect data at rest using application layer encryption.
A Security Engineer is evaluating options for encryption key management.
Why should the Security Engineer choose AWS CloudHSM over AWS KMS for encryption key management in this situation?
B
A global company must mitigate and respond to DDoS attacks at Layers 3, 4 and 7. All of the company's AWS applications are serverless with static content hosted on Amazon S3 using Amazon CloudFront and Amazon Route 53.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
C
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/shield/faqs/
A Security Engineer signed in to the AWS Management Console as an IAM user and switched to the security role IAM role. To perform a maintenance operation, the Security Engineer needs to switch to the maintainer role IAM role, which lists the security role as a trusted entity. The Security Engineer attempts to switch to the maintainer role, but it fails.
What is the likely cause of the failure?
D
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/troubleshoot-iam-policy-issues/
A company is configuring three Amazon EC2 instances with each instance in a separate Availability Zone. The EC2 instances will be used as transparent proxies for outbound internet traffic for ports 80 and 443 so the proxies can block traffic to certain internet destinations as required by the company's security policies. A
Security Engineer completed the following:
Set up the proxy software on the EC2 instances.
✑ Modified the route tables on the private subnets to use the proxy EC2 instances as the default route.
✑ Created a security group rule opening inbound port 80 and 443 TCP protocols on the proxy EC2 instance security group.
However, the proxy EC2 instances are not successfully forwarding traffic to the internet.
What should the Security Engineer do to make the proxy EC2 instances route traffic to the internet?
B
Reference:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/VPC_NAT_Instance.html