A security engineer noticed an anomaly within a company EC2 instance as shown in the image. The engineer must now investigate what is causing the anomaly.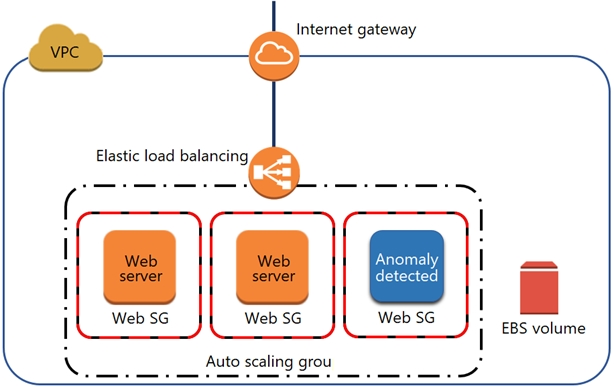
What are the MOST effective steps to take to ensure that the instance is not further manipulated, while allowing the engineer to understand what happened?
D
An external auditor finds that a company's user passwords have no minimum length. The company is currently using two identity providers:
✑ AWS IAM federated with on-premises Active Directory
✑ Amazon Cognito user pools to accessing an AWS Cloud application developed by the company
Which combination of actions should the security engineer take to solve this issue? (Choose two.)
BD
A company's data lake uses Amazon S3 and Amazon Athena. The company's security engineer has been asked to design an encryption solution that meets the company's data protection requirements. The encryption solution must work with Amazon S3 and keys managed by the company. The encryption solution must be protected in a hardware security module that is validated to Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) 140-2 Level 3.
Which solution meets these requirements?
A
A company's security engineer has been asked to monitor and report all AWS account root user activities.
Which of the following would enable the security engineer to monitor and report all root user activities? (Choose two.)
BE
A security engineer needs to ensure their company's use of AWS meets AWS security best practices. As part of this, the AWS account root user must not be used for daily work. The root user must be monitored for use, and the security team must be alerted as quickly as possible if the root user is used.
Which solution meets these requirements?
C
A security engineer is designing an incident response plan to address the risk of a compromised Amazon EC2 instance. The plan must recommend a solution to meet the following requirements:
✑ A trusted forensic environment must be provisioned.
✑ Automated response processes must be orchestrated.
Which AWS services should be included in the plan? (Choose two.)
AB
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/security/how-to-automate-incident-response-in-aws-cloud-for-ec2-instances/
A company's security information events management (SIEM) tool receives new AWS CloudTrail logs from an Amazon S3 bucket that is configured to send all object created event notifications to an Amazon SNS topic. An Amazon SQS queue is subscribed to this SNS topic. The company's SIEM tool then polls this SQS queue for new messages using an IAM role and fetches new log events from the S3 bucket based on the SQS messages.
After a recent security review that resulted in restricted permissions, the SIEM tool has stopped receiving new CloudTrail logs.
Which of the following are possible causes of this issue? (Choose three.)
BDE
A security engineer has noticed that VPC Flow Logs are getting a lot of REJECT traffic originating from a single Amazon EC2 instance in an Auto Scaling group.
The security engineer is concerned that this EC2 instance may be compromised.
What immediate action should the security engineer take?
B
A company's director of information security wants a daily email report from AWS that contains recommendations for each company account to meet AWS
Security best practices.
Which solution would meet these requirements?
D
A company is using AWS Organizations to manage multiple AWS member accounts. All of these accounts have Amazon GuardDuty enabled in all Regions. The company's AWS Security Operations Center has a centralized security account for logging and monitoring. One of the member accounts has received an excessively high bill. A security engineer discovers that a compromised Amazon EC2 instance is being used to mine cryptocurrency. The Security Operations
Center did not receive a GuardDuty finding in the central security account, but there was a GuardDuty finding in the account containing the compromised EC2 instance. The security engineer needs to ensure all GuardDuty findings are available in the security account.
What should the security engineer do to resolve this issue?
B