You plan to map a network drive from several computers that run Windows 10 to Azure Storage.
You need to create a storage solution in Azure for the planned mapped drive.
What should you create?
Answer:
C
Azure Files is Microsoft's easy-to-use cloud file system. Azure file shares can be seamlessly used in Windows and Windows Server.
To use an Azure file share with Windows, you must either mount it, which means assigning it a drive letter or mount point path, or access it via its UNC path.
Unlike other SMB shares you may have interacted with, such as those hosted on a Windows Server, Linux Samba server, or NAS device, Azure file shares do not currently support Kerberos authentication with your Active Directory (AD) or Azure Active Directory (AAD) identity, although this is a feature we are working on.
Instead, you must access your Azure file share with the storage account key for the storage account containing your Azure file share. A storage account key is an administrator key for a storage account, including administrator permissions to all files and folders within the file share you're accessing, and for all file shares and other storage resources (blobs, queues, tables, etc) contained within your storage account.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/files/storage-how-to-use-files-windows
HOTSPOT -
You plan to implement an Azure database solution.
You need to implement a database solution that meets the following requirements:
✑ Can add data concurrently from multiple regions
✑ Can store JSON documents
Which database service should you deploy? To answer, select the appropriate service in the answer area.
Hot Area: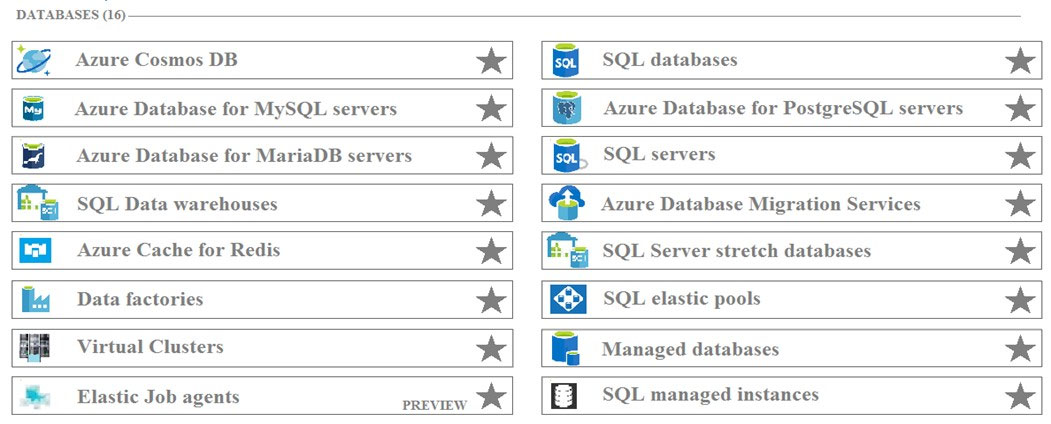
Answer:
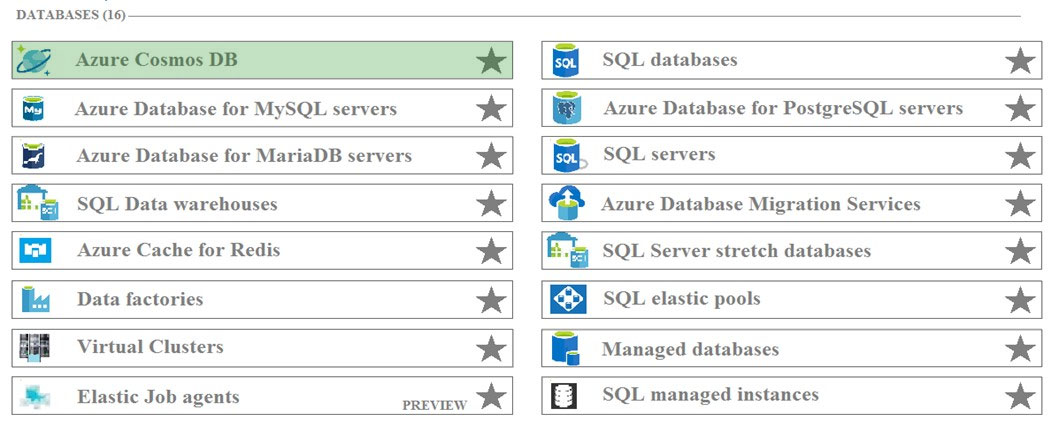
Azure Cosmos DB is Microsoft's globally distributed, multi-model database service. With a click of a button, Cosmos DB enables you to elastically and independently scale throughput and storage across any number of Azure regions worldwide.
Azure Cosmos DB is a great way to store unstructured and JSON data. Combined with Azure Functions, Cosmos DB makes storing data quick and easy with much less code than required for storing data in a relational database.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/cosmos-db/introduction https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/functions-integrate-store-unstructured-data-cosmosdb?tabs=csharp
Your company plans to start using Azure and will migrate all its network resources to Azure.
You need to start the planning process by exploring Azure.
What should you create first?
Answer:
A
The first thing you create in Azure is a subscription. You can think of an Azure subscription as an 'Azure account'. You get billed per subscription.
A subscription is an agreement with Microsoft to use one or more Microsoft cloud platforms or services, for which charges accrue based on either a per-user license fee or on cloud-based resource consumption.
✑ Microsoft's Software as a Service (SaaS)-based cloud offerings (Office 365, Intune/EMS, and Dynamics 365) charge per-user license fees.
✑ Microsoft's Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) cloud offerings (Azure) charge based on cloud resource consumption.
You can also use a trial subscription, but the subscription expires after a specific amount of time or consumption charges. You can convert a trial subscription to a paid subscription.
Organizations can have multiple subscriptions for Microsoft's cloud offerings.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/office365/enterprise/subscriptions-licenses-accounts-and-tenants-for-microsoft-cloud-offerings
HOTSPOT -
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: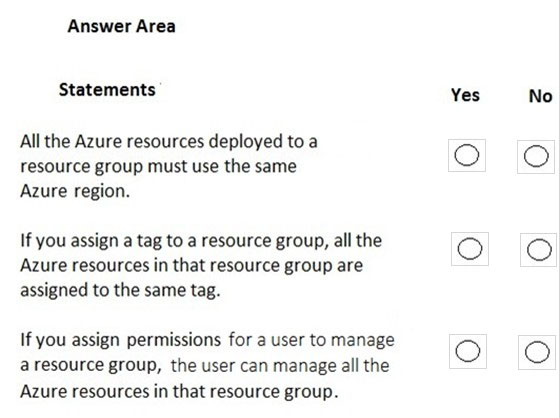
Answer:
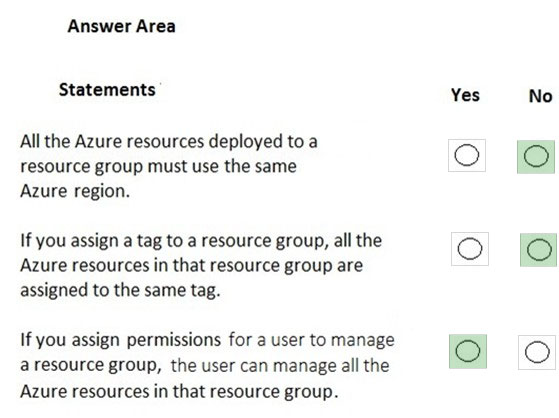
Box 1: No -
Azure resources deployed to a single resource group can be located in different regions. The resource group only contains metadata about the resources it contains.
When creating a resource group, you need to provide a location for that resource group. You may be wondering, "Why does a resource group need a location?
And, if the resources can have different locations than the resource group, why does the resource group location matter at all?" The resource group stores metadata about the resources. When you specify a location for the resource group, you're specifying where that metadata is stored. For compliance reasons, you may need to ensure that your data is stored in a particular region.
Box 2: No -
Tags for Resources are not inherited by default from their Resource Group
Box 3: Yes -
A resource group can be used to scope access control for administrative actions. By default, permissions set at the resource level are inherited by the resources in the resource group.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-resource-manager/resource-group-overview
HOTSPOT -
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.
Hot Area: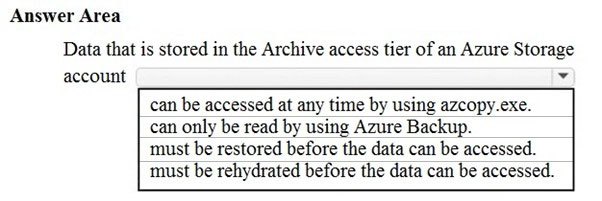
Answer:
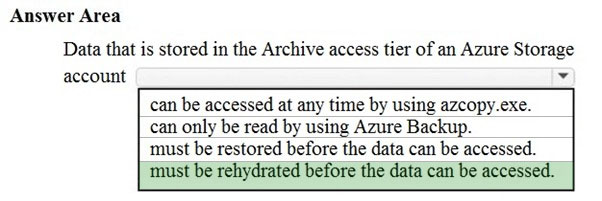
Azure storage offers different access tiers: hot, cool and archive.
The archive access tier has the lowest storage cost. But it has higher data retrieval costs compared to the hot and cool tiers. Data in the archive tier can take several hours to retrieve.
While a blob is in archive storage, the blob data is offline and can't be read, overwritten, or modified. To read or download a blob in archive, you must first rehydrate it to an online tier.
Example usage scenarios for the archive access tier include:
✑ Long-term backup, secondary backup, and archival datasets
✑ Original (raw) data that must be preserved, even after it has been processed into final usable form.
✑ Compliance and archival data that needs to be stored for a long time and is hardly ever accessed.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-blob-storage-tiers?tabs=azure-portal#archive-access-tier
HOTSPOT -
You plan to deploy a critical line-of-business application to Azure.
The application will run on an Azure virtual machine.
You need to recommend a deployment solution for the application. The solution must provide a guaranteed availability of 99.99 percent.
What is the minimum number of virtual machines and the minimum number of availability zones you should recommend for the deployment? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: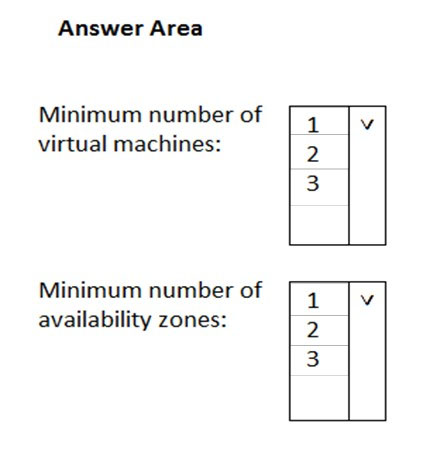
Answer:

You need a minimum of two virtual machines with each one located in a different availability zone.
Availability Zones is a high-availability offering that protects your applications and data from datacenter failures. Availability Zones are unique physical locations within an Azure region. Each zone is made up of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking. To ensure resiliency, there's a minimum of three separate zones in all enabled regions. The physical separation of Availability Zones within a region protects applications and data from datacenter failures. Zone-redundant services replicate your applications and data across Availability Zones to protect from single-points-of-failure. With Availability
Zones, Azure offers industry best 99.99% VM uptime SLA.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/availability-zones/az-overview
Which Azure service should you use to collect events from multiple resources into a centralized repository?
Answer:
A
Azure Event Hubs is a big data streaming platform and event ingestion service. It can receive and process millions of events per second. Data sent to an event hub can be transformed and stored by using any real-time analytics provider or batching/storage adapters.
Azure Event Hubs can be used to ingest, buffer, store, and process your stream in real time to get actionable insights. Event Hubs uses a partitioned consumer model, enabling multiple applications to process the stream concurrently and letting you control the speed of processing.
Azure Event Hubs can be used to capture your data in near-real time in an Azure Blob storage or Azure Data Lake Storageג€‰for long-term retention or micro-batch processing.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/event-hubs/event-hubs-about
HOTSPOT -
To complete the sentence, select the appropriate option in the answer area.
Hot Area:
Answer:

Availability Zones is a high-availability offering that protects your applications and data from datacenter failures. Availability Zones are unique physical locations within an Azure region.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/availability-zones/az-overview
HOTSPOT -
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: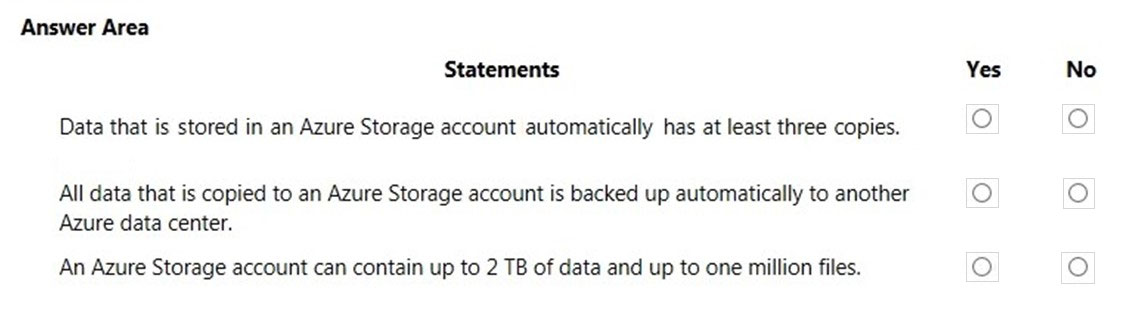
Answer:
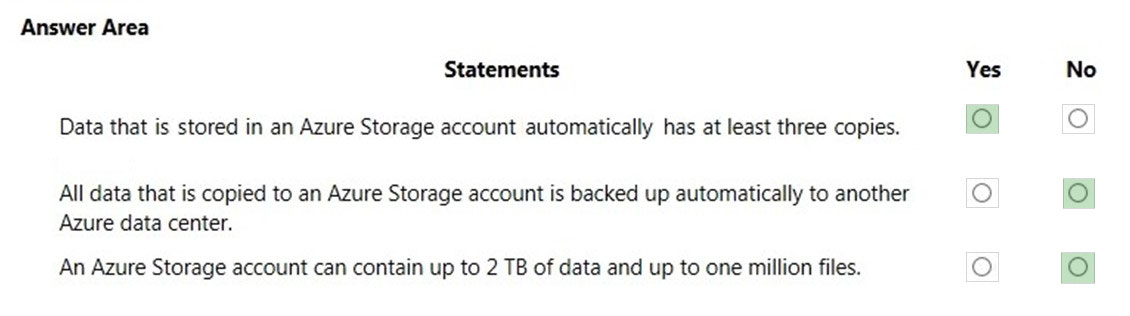
Box 1: Yes -
There are different replication options available with a storage account. The 'minimum' replication option is Locally Redundant Storage (LRS). With LRS, data is replicated synchronously three times within the primary region.
Box 2: No -
Data is not backed up automatically to another Azure Data Center although it can be depending on the replication option configured for the account. Locally
Redundant Storage (LRS) is the default which maintains three copies of the data in the data center.
Geo-redundant storage (GRS) has cross-regional replication to protect against regional outages. Data is replicated synchronously three times in the primary region, then replicated asynchronously to the secondary region.
Box 3: No -
The limits are much higher than that. The current storage limit is 2 PB for US and Europe, and 500 TB for all other regions (including the UK) with no limit on the number of files.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/common/storage-account-overview
HOTSPOT -
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Answer:
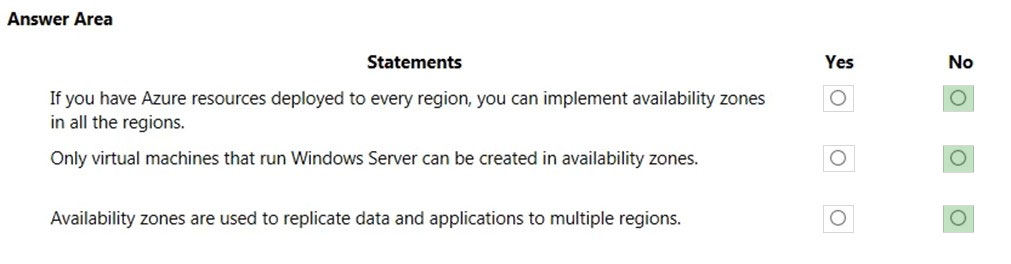
Box 1: No -
Not all Azure regions support availability zones.
Box 2: No -
Regions that support availability zones support Linux virtual machines.
Box 3: Yes -
Availability Zones is a high-availability offering that protects your applications and data from datacenter failures. Availability Zones are unique physical locations within an Azure region. Each zone is made up of one or more datacenters equipped with independent power, cooling, and networking. To ensure resiliency, there's a minimum of three separate zones in all enabled regions. The physical separation of Availability Zones within a region protects applications and data from datacenter failures. Zone-redundant services replicate your applications and data across Availability Zones to protect from single-points-of-failure. With Availability
Zones, Azure offers industry best 99.99% VM uptime SLA.
References:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/azure/availability-zones/az-overview