Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are developing a website that will run as an Azure Web App. Users will authenticate by using their Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) credentials.
You plan to assign users one of the following permission levels for the website: admin, normal, and reader. A user's Azure AD group membership must be used to determine the permission level.
You need to configure authorization.
Solution:
✑ Create a new Azure AD application. In the application's manifest, define application roles that match the required permission levels for the application.
✑ Assign the appropriate Azure AD group to each role. In the website, use the value of the roles claim from the JWT for the user to determine permissions.
Does the solution meet the goal?
Answer:
B
To configure Manifest to include Group Claims in Auth Token
1. Go to Azure Active Directory to configure the Manifest. Click on Azure Active Directory, and go to App registrations to find your application:
2. Click on your application (or search for it if you have a lot of apps) and edit the Manifest by clicking on it.
3. Locate the ג€groupMembershipClaimsג€ setting. Set its value to either ג€SecurityGroupג€ or ג€Allג€. To help you decide which:
✑ ג€SecurityGroupג€ - groups claim will contain the identifiers of all security groups of which the user is a member.
✑ ג€Allג€ - groups claim will contain the identifiers of all security groups and all distribution lists of which the user is a member
Now your application will include group claims in your manifest and you can use this fact in your code.
Reference:
https://blogs.msdn.microsoft.com/waws/2017/03/13/azure-app-service-authentication-aad-groups/
DRAG DROP -
You are developing an application to securely transfer data between on-premises file systems and Azure Blob storage. The application stores keys, secrets, and certificates in Azure Key Vault. The application uses the Azure Key Vault APIs.
The application must allow recovery of an accidental deletion of the key vault or key vault objects. Key vault objects must be retained for 90 days after deletion.
You need to protect the key vault and key vault objects.
Which Azure Key Vault feature should you use? To answer, drag the appropriate features to the correct actions. Each feature may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place:
Answer:

Box 1: Soft delete -
When soft-delete is enabled, resources marked as deleted resources are retained for a specified period (90 days by default). The service further provides a mechanism for recovering the deleted object, essentially undoing the deletion.
Box 2: Purge protection -
Purge protection is an optional Key Vault behavior and is not enabled by default. Purge protection can only be enabled once soft-delete is enabled.
When purge protection is on, a vault or an object in the deleted state cannot be purged until the retention period has passed. Soft-deleted vaults and objects can still be recovered, ensuring that the retention policy will be followed.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/key-vault/general/soft-delete-overview
You provide an Azure API Management managed web service to clients. The back-end web service implements HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS).
Every request to the backend service must include a valid HTTP authorization header.
You need to configure the Azure API Management instance with an authentication policy.
Which two policies can you use? Each correct answer presents a complete solution.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Answer:
CD
DRAG DROP -
You are developing an ASP.NET Core website that can be used to manage photographs which are stored in Azure Blob Storage containers.
Users of the website authenticate by using their Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) credentials.
You implement role-based access control (RBAC) role permissions on the containers that store photographs. You assign users to RBAC roles.
You need to configure the website's Azure AD Application so that user's permissions can be used with the Azure Blob containers.
How should you configure the application? To answer, drag the appropriate setting to the correct location. Each setting can be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Select and Place: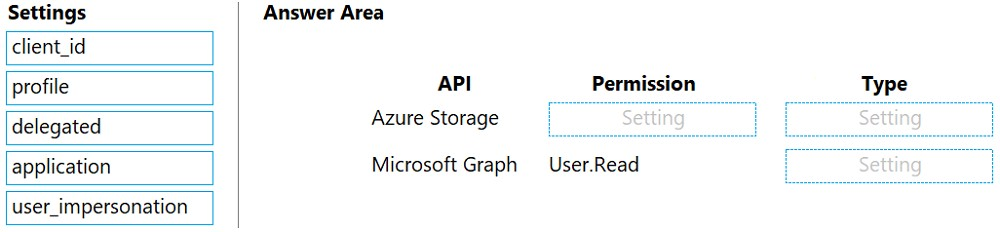
Answer:
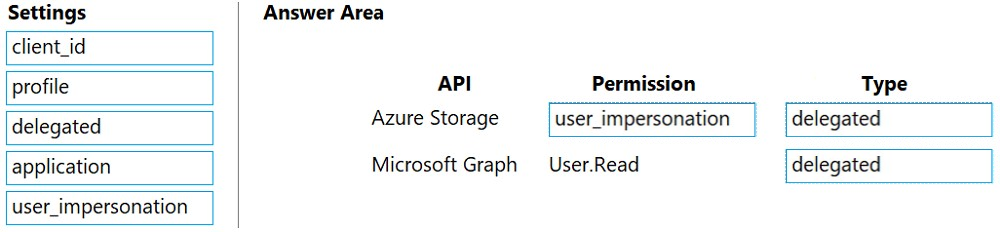
Box 1: user_impersonation -
Box 2: delegated -
Example:
1. Select the API permissions section
2. Click the Add a permission button and then:
Ensure that the My APIs tab is selected
3. In the list of APIs, select the API TodoListService-aspnetcore.
4. In the Delegated permissions section, ensure that the right permissions are checked: user_impersonation.
5. Select the Add permissions button.
Box 3: delegated -
Example -
1. Select the API permissions section
2. Click the Add a permission button and then,
Ensure that the Microsoft APIs tab is selected
3. In the Commonly used Microsoft APIs section, click on Microsoft Graph
4. In the Delegated permissions section, ensure that the right permissions are checked: User.Read. Use the search box if necessary.
5. Select the Add permissions button
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/samples/azure-samples/active-directory-dotnet-webapp-webapi-openidconnect-aspnetcore/calling-a-web-api-in-an-aspnet-core- web-application-using-azure-ad/
HOTSPOT -
You are developing an ASP.NET Core app that includes feature flags which are managed by Azure App Configuration. You create an Azure App Configuration store named AppFeatureFlagStore that contains a feature flag named Export.
You need to update the app to meet the following requirements:
✑ Use the Export feature in the app without requiring a restart of the app.
✑ Validate users before users are allowed access to secure resources.
✑ Permit users to access secure resources.
How should you complete the code segment? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area: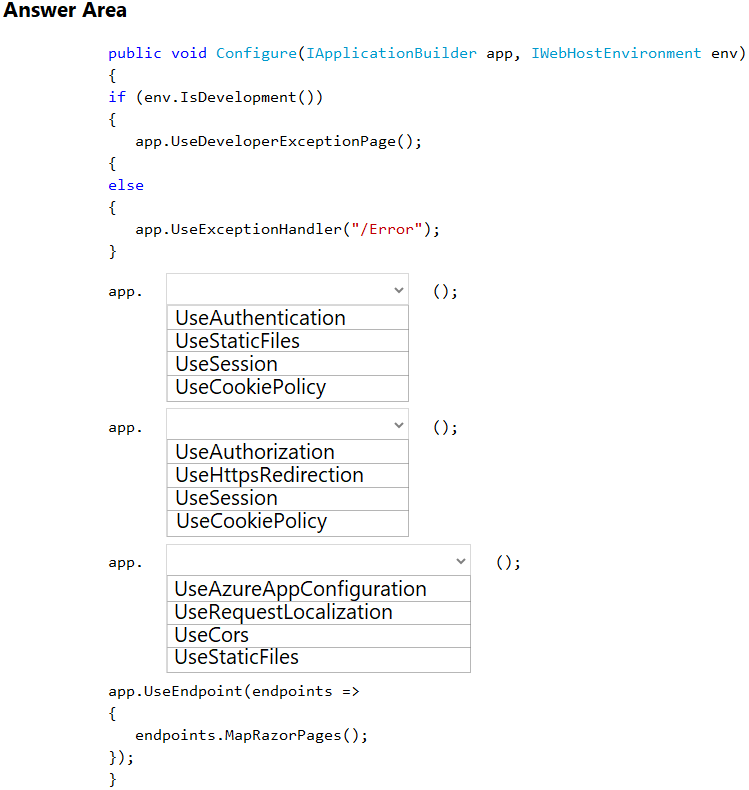
Answer:
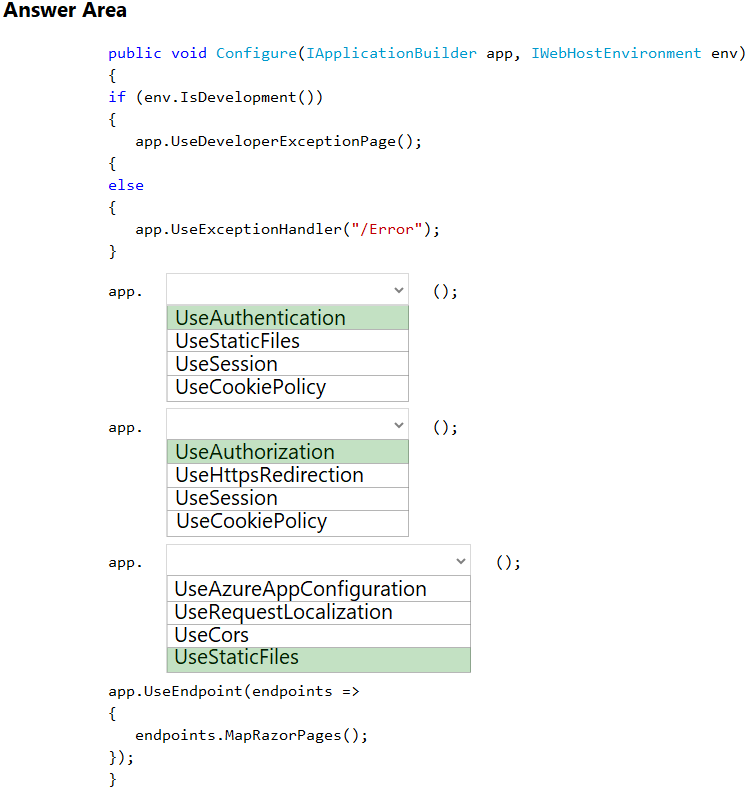
Box 1: UseAuthentication -
Need to validate users before users are allowed access to secure resources.
UseAuthentication adds the AuthenticationMiddleware to the specified IApplicationBuilder, which enables authentication capabilities.
Box 2: UseAuthorization -
Need to permit users to access secure resources.
UseAuthorization adds the AuthorizationMiddleware to the specified IApplicationBuilder, which enables authorization capabilities.
Box 3: UseStaticFiles -
Need to use the Export feature in the app without requiring a restart of the app.
UseStaticFiles enables static file serving for the current request path
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/api/microsoft.aspnetcore.builder.iapplicationbuilder?view=aspnetcore-5.0
You have an application that includes an Azure Web app and several Azure Function apps. Application secrets including connection strings and certificates are stored in Azure Key Vault.
Secrets must not be stored in the application or application runtime environment. Changes to Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) must be minimized.
You need to design the approach to loading application secrets.
What should you do?
Answer:
C
Use Key Vault references for App Service and Azure Functions.
Key Vault references currently only support system-assigned managed identities. User-assigned identities cannot be used.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/app-service/app-service-key-vault-references
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are developing a medical records document management website. The website is used to store scanned copies of patient intake forms.
If the stored intake forms are downloaded from storage by a third party, the contents of the forms must not be compromised.
You need to store the intake forms according to the requirements.
Solution:
1. Create an Azure Key Vault key named skey.
2. Encrypt the intake forms using the public key portion of skey.
3. Store the encrypted data in Azure Blob storage.
Does the solution meet the goal?
Answer:
A
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are developing a medical records document management website. The website is used to store scanned copies of patient intake forms.
If the stored intake forms are downloaded from storage by a third party, the contents of the forms must not be compromised.
You need to store the intake forms according to the requirements.
Solution:
1. Create an Azure Cosmos DB database with Storage Service Encryption enabled.
2. Store the intake forms in the Azure Cosmos DB database.
Does the solution meet the goal?
Answer:
B
Instead use an Azure Key vault and public key encryption. Store the encrypted from in Azure Storage Blob storage.
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You are developing a medical records document management website. The website is used to store scanned copies of patient intake forms.
If the stored intake forms are downloaded from storage by a third party, the contents of the forms must not be compromised.
You need to store the intake forms according to the requirements.
Solution: Store the intake forms as Azure Key Vault secrets.
Does the solution meet the goal?
Answer:
B
Instead use an Azure Key vault and public key encryption. Store the encrypted from in Azure Storage Blob storage.
HOTSPOT -
You plan to deploy a new application to a Linux virtual machine (VM) that is hosted in Azure.
The entire VM must be secured at rest by using industry-standard encryption technology to address organizational security and compliance requirements.
You need to configure Azure Disk Encryption for the VM.
How should you complete the Azure CLI commands? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Hot Area:
Answer:
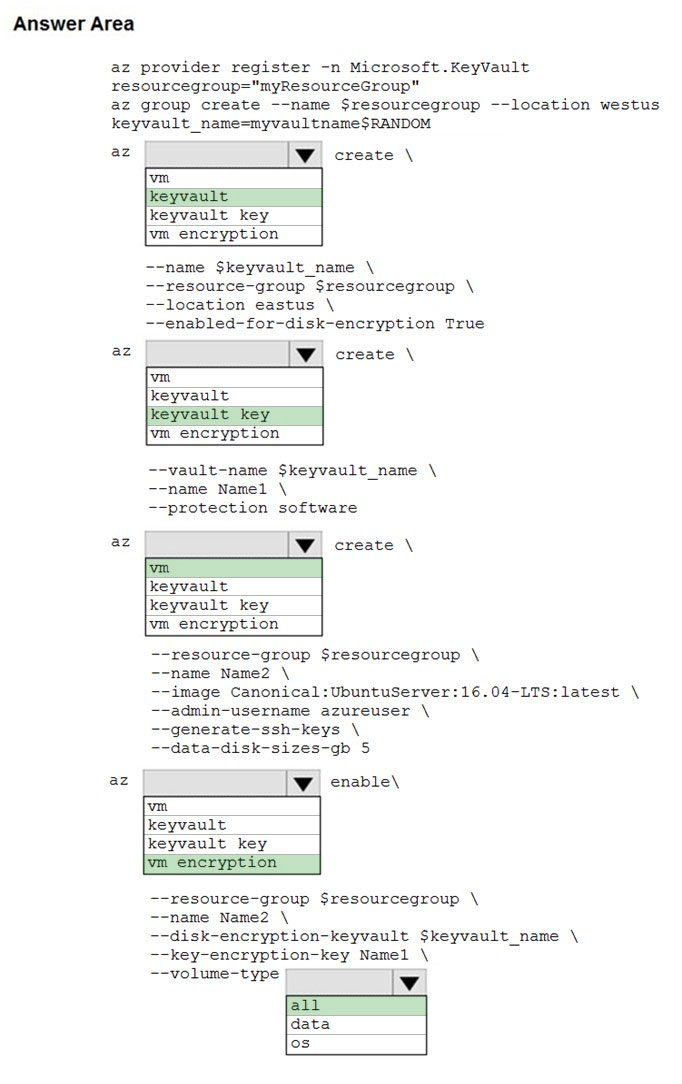
Box 1: keyvault -
Create an Azure Key Vault with az keyvault create and enable the Key Vault for use with disk encryption. Specify a unique Key Vault name for keyvault_name as follows: keyvault_name=myvaultname$RANDOM az keyvault create \
--name $keyvault_name \
--resource-group $resourcegroup \
--location eastus \
--enabled-for-disk-encryption True
Box 2: keyvault key -
The Azure platform needs to be granted access to request the cryptographic keys when the VM boots to decrypt the virtual disks. Create a cryptographic key in your Key Vault with az keyvault key create. The following example creates a key named myKey: az keyvault key create \
--vault-name $keyvault_name \
--name myKey \
--protection software
Box 3: vm -
Create a VM with az vm create. Only certain marketplace images support disk encryption. The following example creates a VM named myVM using an Ubuntu
16.04 LTS image:
az vm create \
--resource-group $resourcegroup \
--name myVM \
--image Canonical:UbuntuServer:16.04-LTS:latest \
--admin-username azureuser \
--generate-ssh-keys \
Box 4: vm encryption -
Encrypt your VM with az vm encryption enable:
az vm encryption enable \
--resource-group $resourcegroup \
--name myVM \
--disk-encryption-keyvault $keyvault_name \
--key-encryption-key myKey \
--volume-type all
Note: seems to an error in the question. Should have enable instead of create.
Box 5: all -
Encrypt both data and operating system.
Reference:
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/disk-encryption-cli-quickstart