An engineer configures a WLAN with fast transition enabled. Some legacy clients fail to connect to this WLAN.
Which feature allows the legacy clients to connect while still allowing other clients to use fast transition based on their OUIs?
C
What are two common sources of interference for Wi-Fi networks? (Choose two.)
BE
Which two pieces of information are necessary to compute SNR? (Choose two.)
BD
Reference:
https://community.cisco.com/t5/wireless-mobility-documents/snr-rssi-eirp-and-free-space-path-loss/ta-p/3128478
Which OSPF network types are compatible and allow communication through the two peering devices?
B
Reference:
https://www.freeccnaworkbook.com/workbooks/ccna/configuring-ospf-network-types
Refer to the exhibit.
Which statement about the OSPF debug output is true?
A
Which statement about multicast RPs is true?
D
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios/solutions_docs/ip_multicast/White_papers/rps.html
To increase total throughput and redundancy on the links between the wireless controller and switch, the customer enabled LAG on the wireless controller.
Which EtherChannel mode must be configured on the switch to allow the WLC to connect?
C
Reference:
https://community.cisco.com/t5/wireless-mobility-documents/lag-link-aggregation/ta-p/3128669
Based on this interface configuration, what is the expected state of OSPF adjacency?
B
Refer to the exhibit.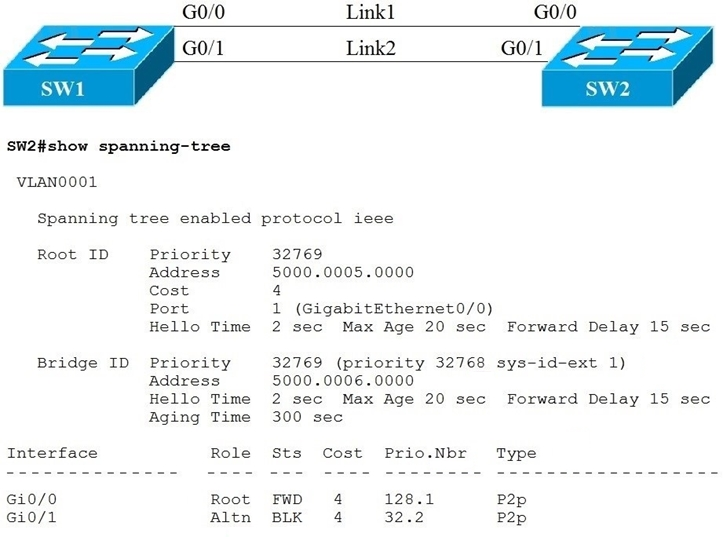
Link1 is a copper connection and Link2 is a fiber connection. The fiber port must be the primary port for all forwarding. The output of the show spanning-tree command on SW2 shows that the fiber port is blocked by spanning tree. An engineer enters the spanning-tree port-priority 32 command on G0/1 on SW2, but the port remains blocked.
Which command should be entered on the ports that are connected to Link2 to resolve the issue?
B
Which behavior can be expected when the HSRP version is changed from 1 to 2?
C