How is a sub-second failure of a transport link detected in a Cisco SD-WAN network?
B
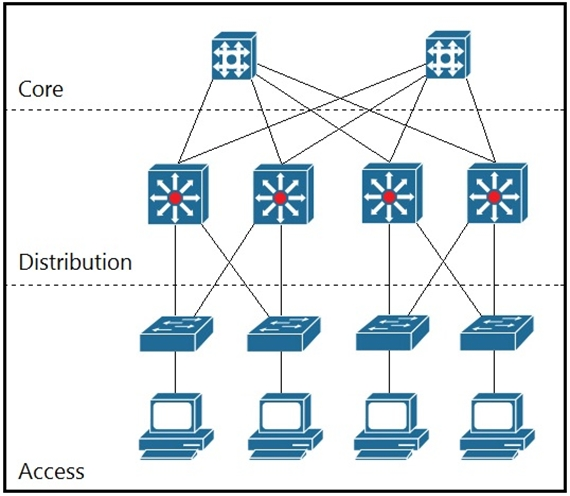
Refer to the exhibit. Which two solutions maximize the use of the links between the core and distribution layers? (Choose two.)
AB
A customer's current Layer 2 infrastructure is running Spanning Tree 802.1d, and all configuration changes are manually implemented on each switch. An architect must redesign the Layer 2 domain to achieve these goals:
* reduce the impact of topology changes
* reduce the time spent on network administration
* reduce manual configuration errors
Which two solutions should the architect include in the new design? (Choose two.)
CD
Which component is part of the Cisco SD-Access overlay architecture?
D
How are wireless endpoints registered in the HTDB in a Cisco SD-Access architecture?
B
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/Campus/cisco-sda-design-guide.html
What is the purpose of a Cisco SD-Access underlay network?
C
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the components in a Cisco SD-Access architecture from the left onto their descriptions on the right.
Select and Place: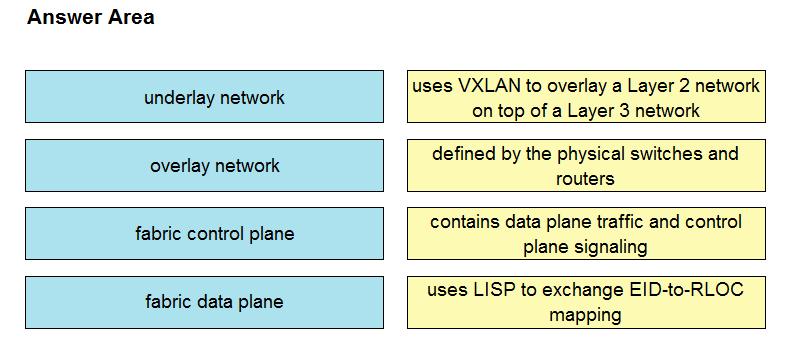
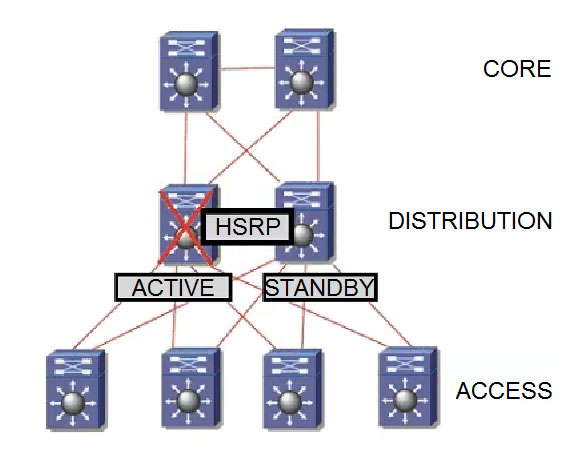
Refer to the exhibit. The distribution switches serve as the Layer 3 boundary. HSRP preemption is enabled. When the primary switch comes back after a failure, traffic is initially dropped. Which solution must be implemented to improve the design?
C

Refer to the exhibit. Where must an architect plan for route summarization for the topology?
D
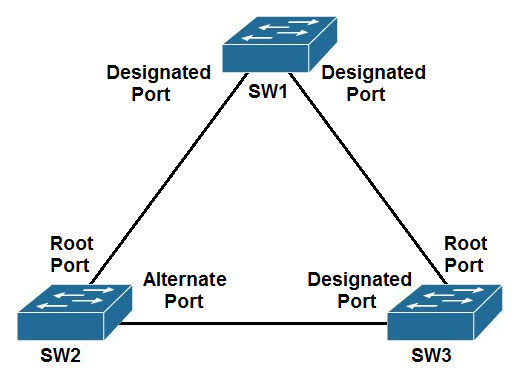
Refer to the exhibit. The connection between SW2 and SW3 is fiber and occasionally experiences unidirectional link failure. An architect must optimize the network to reduce the change of Layer 2 forwarding loops when the link fails. Which solution should the architect include?
D