
Refer to the exhibit. An administrator configured a Cisco router for TACACS authentication, but the router is using the local enable password instead. Which action resolves the issue?
D
Reference:
https://community.cisco.com/t5/network-access-control/problem-setting-7606-router-for-tacacs-authentication/td-p/2316903
An administrator attempts to download the .pack NBAR2 file using TFTP from the CPE router to another device over the Gi0/0 interface. The CPE is configured as below: hostname CPE
!
ip access-list extended WAN
<`¦>
remark => All UDP rules below for WAN ID: S421T18E58F90
permit udp any eq domain any
permit udp any any eq tftp
deny udp any any
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
<`¦>
ip access-group WAN in
<`¦>
!
tftp-server flash:pp-adv-csr1000v-1612.1a-37-53.0.0.pack
The transfer fails. Which action resolves this issue?
C
A network administrator must optimize the segment size of the TCP packet on the DMVPN IPsec protected tunnel interface, which carries application traffic from the head office to a designated branch. The TCP segment size must not overwhelm the MTU of the outbound link. Which configuration must be applied to the router to improve the application performance?
B
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/sec_conn_dmvpn/configuration/15-mt/sec-conn-dmvpn-15-mt-book/sec-conn-dmvpn-dmvpn.html
In a DMVPN network, the Spoke1 user observed that the voice traffic is coming to Spoke2 users via the hub router. Which command is required on both spoke routers to communicate directly to one another?
B
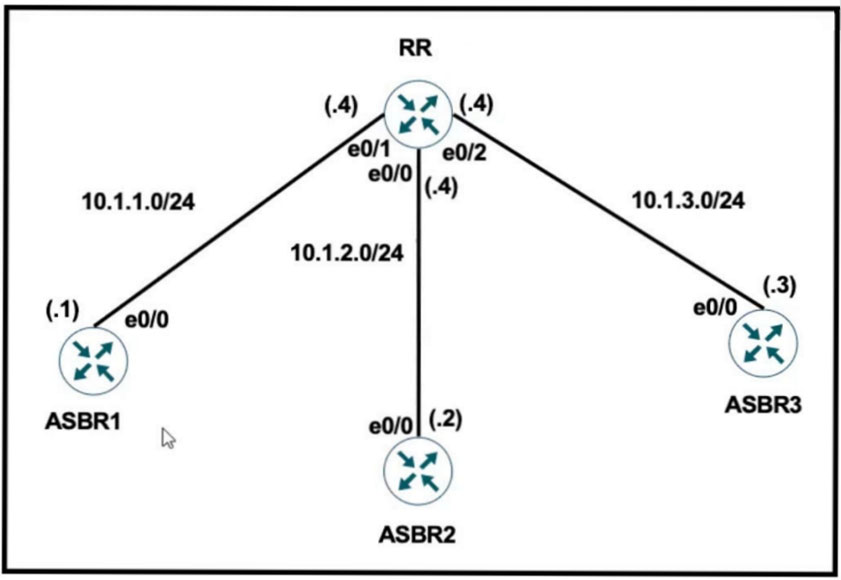
Refer to the exhibit.
RR Configuration:
router bgp 100
neighbor IBGP peer-group
neighbor IBGP route-reflector-client
neighbor 10.1.1.1 remote-as 100
neighbor 10.1.2.2 remote-as 100
neighbor 10.1.3.3 remote-as 100
The network administrator configured the network to establish connectivity between all devices and notices that the ASBRs do not have routes for each other.
Which set of configurations resolves this issue?
D

Refer to the exhibit. A prefix list is created to filter routes inbound to an EIGRP process except for network 10 prefixes. After the prefix list is applied, no network 10 prefixes are visible in the routing table from EIGRP. Which configuration resolves the issue?
D
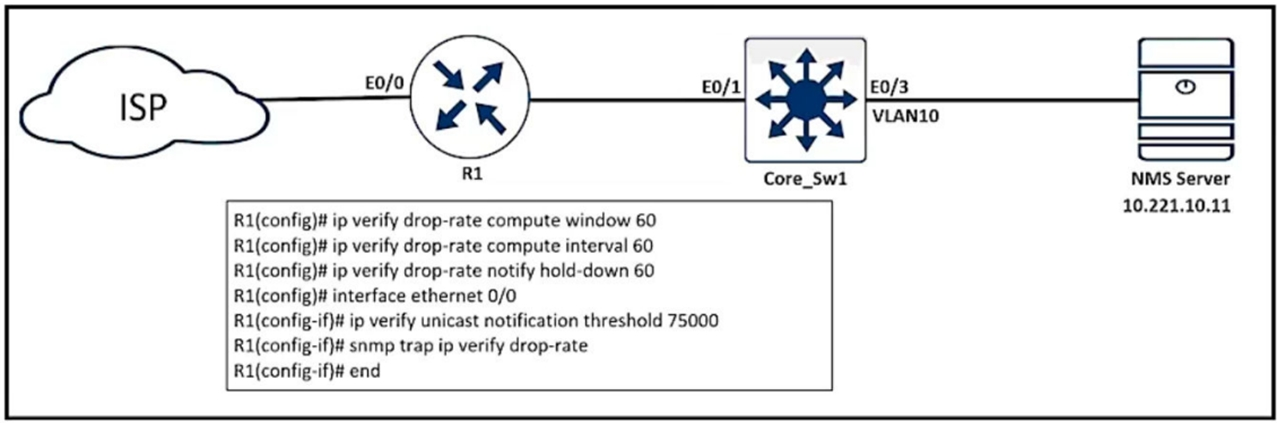
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer configured SNMP traps to record spoofed packets drop of more than 48000 a minute on the ethernet0/0 interface. During an IP spoofing attack, the engineer noticed that no notifications have been received by the SNMP server. Which configuration resolves the issue on R1?
A
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/sec_data_urpf/configuration/12-4t/sec-data-urpf-12-4t-book/sec-urpf-mib.html
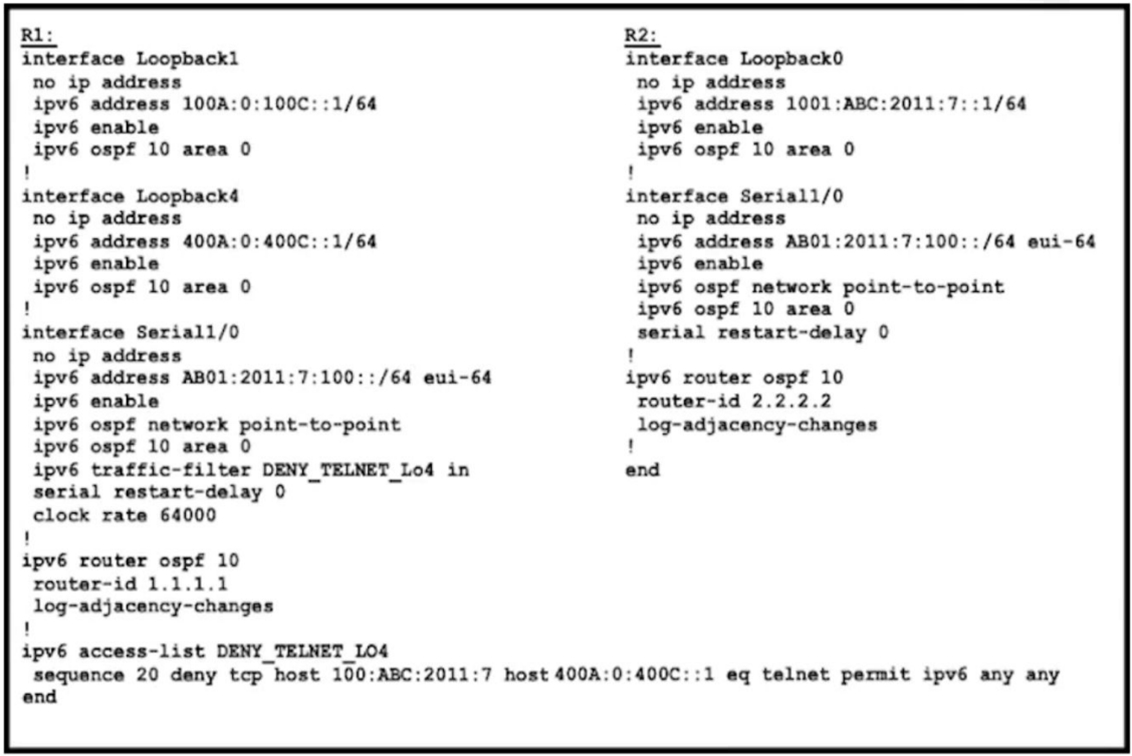
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer implemented an access list on R1 to allow anyone to Telnet except R2 Loopback0 to R1 Loopback4. How must sequence 20 be replaced on the R1 access list to resolve the issue?
D
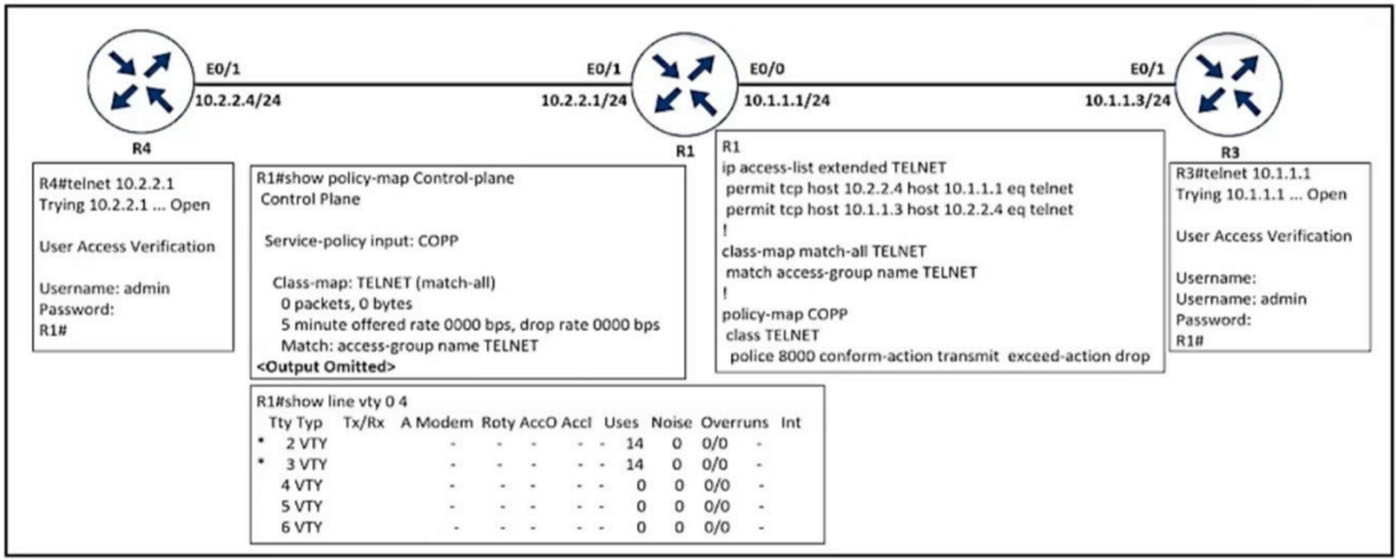
Refer to the exhibit. An engineer implemented CoPP to limit Telnet traffic to protect the router CPU. It was noticed that the Telnet traffic did not pass through
CoPP. Which configuration resolves the issue?
C
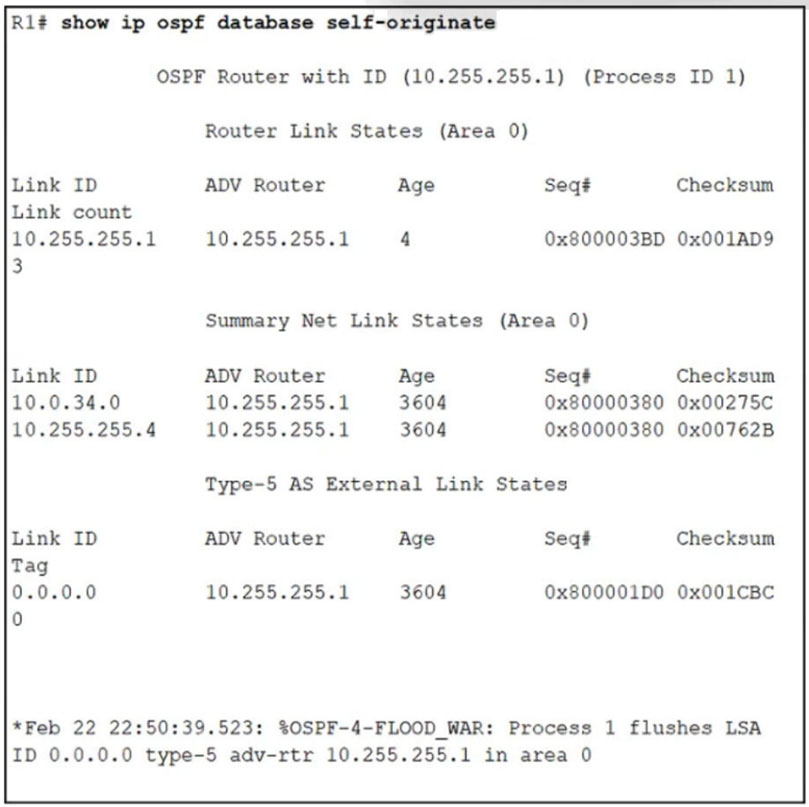
Refer to the exhibit. After configuring OSPF in R1, some external destinations in the network became unreachable. Which action resolves the issue?
C
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/open-shortest-path-first-ospf/118880-technote-ospf-00.html