Which event artifact is used to identify HTTP GET requests for a specific file?
D
What should a security analyst consider when comparing inline traffic interrogation with traffic tapping to determine which approach to use in the network?
A
At which layer is deep packet inspection investigated on a firewall?
C
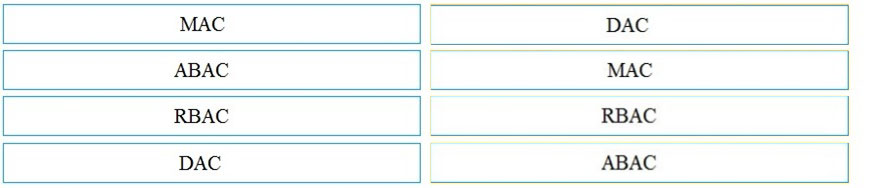
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the access control models from the left onto its corresponding descriptions on the right.
Select and Place: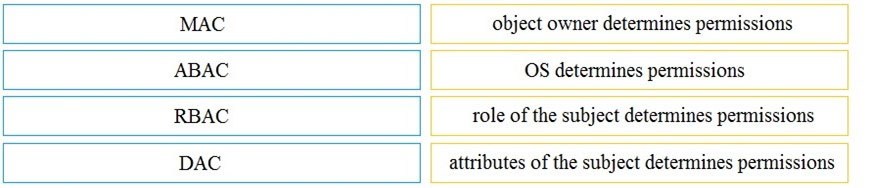
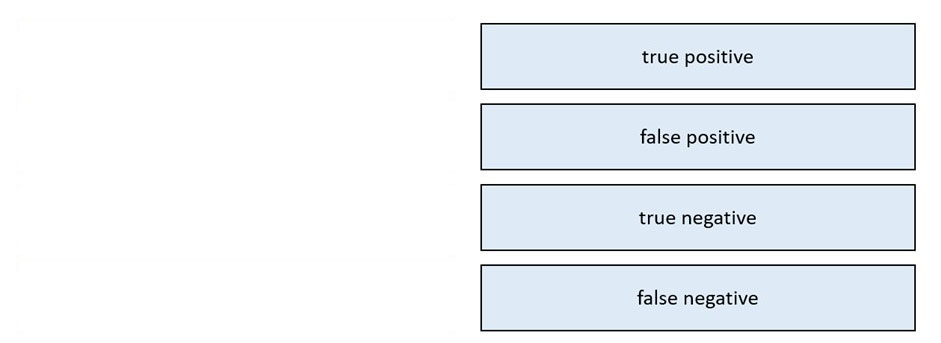
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the event term from the left onto the description on the right.
Select and Place: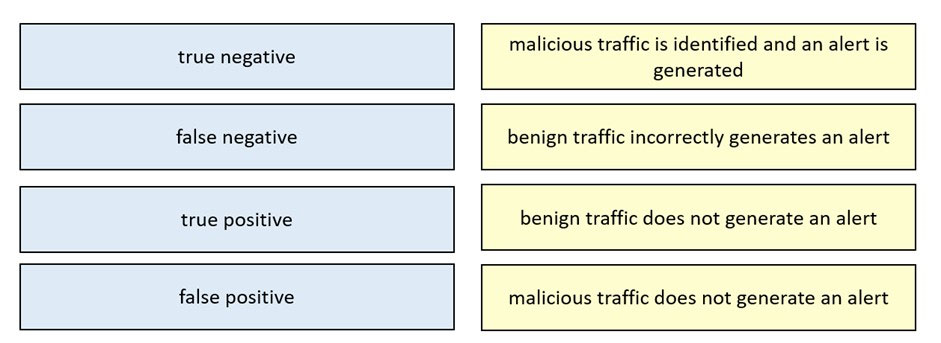
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/security/ips-4200-series-sensors/13876-f-pos.html

Refer to the exhibit. What is occurring?
D
Reference:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/http/http_requests.htm
What is a difference between data obtained from Tap and SPAN ports?
D
Reference:
https://www.gigamon.com/resources/resource-library/white-paper/to-tap-or-to-span.html
DRAG DROP -
Drag and drop the data source from the left onto the data type on the right.
Select and Place: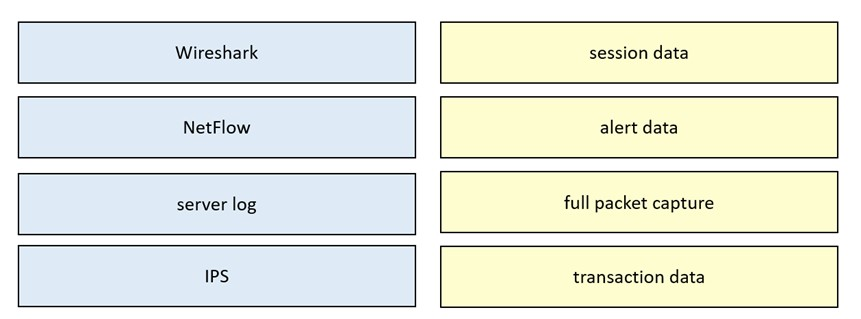
A threat actor penetrated an organization's network. Using the 5-tuple approach, which data points should the analyst use to isolate the compromised host in a grouped set of logs?
D
Reference:
https://blogs.cisco.com/security/the-dreaded-5-tuple
What is a difference between an inline and a tap mode traffic monitoring?
C
Reference:
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/security/firepower/650/configuration/guide/fpmc-config-guide-v65/ inline_sets_and_passive_interfaces_for_firepower_threat_defense.html