A company uses an Amazon EMR cluster to process data once a day. The raw data comes from Amazon S3, and the resulting processed data is also stored in
Amazon S3. The processing must complete within 4 hours; currently, it only takes 3 hours. However, the processing time is taking 5 to 10 minutes longer each week due to an increasing volume of raw data.
The team is also concerned about rising costs as the compute capacity increases. The EMR cluster is currently running on three m3.xlarge instances (one master and two core nodes).
Which of the following solutions will reduce costs related to the increasing compute needs?
B
A company is building an AWS landing zone and has asked a Solutions Architect to design a multi-account access strategy that will allow hundreds of users to use corporate credentials to access the AWS Console. The company is running a Microsoft Active Directory, and users will use an AWS Direct Connect connection to connect to AWS. The company also wants to be able to federate to third-party services and providers, including custom applications.
Which solution meets the requirements by using the LEAST amount of management overhead?
D
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/ru/blogs/security/aws-federated-authentication-with-active-directory-federation-services-ad-fs/
A Solutions Architect is designing a network solution for a company that has applications running in a data center in Northern Virginia. The applications in the company's data center require predictable performance to applications running in a virtual private cloud (VPC) located in us-east-1, and a secondary VPC in us- west-2 within the same account. The company data center is collocated in an AWS Direct Connect facility that serves the us-east-1 region. The company has already ordered an AWS Direct Connect connection and a cross-connect has been established.
Which solution will meet the requirements at the LOWEST cost?
A
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/new-aws-direct-connect-gateway-inter-region-vpc-access/
A company has a web service deployed in the following two AWS Regions: us-west-2 and us-est-1. Each AWS region runs an identical version of the web service.
Amazon Route 53 is used to route customers to the AWS Region that has the lowest latency.
The company wants to improve the availability of the web service in case an outage occurs in one of the two AWS Regions.
A Solutions Architect has recommended that a Route 53 health check be performed. The health check must detect a specific text on an endpoint.
What combination of conditions should the endpoint meet to pass the Route 53 health check? (Choose two.)
CD
A company operating a website on AWS requires high levels of scalability, availability, and performance. The company is running a Ruby on Rails application on
Amazon EC2. It has a data tier on MySQL 5.6 on Amazon EC2 using 16 TB of Amazon EBS storage Amazon CloudFront is used to cache application content.
The Operations team is reporting continuous and unexpected growth of EBS volumes assigned to the MySQL database. The Solutions Architect has been asked to design a highly scalable, highly available, and high-performing solution.
Which solution is the MOST cost-effective at scale?
C
The Security team needs to provide a team of interns with an AWS environment so they can build a serverless video transcoding application. The project will use
Amazon S3, AWS Lambda, Amazon API Gateway, Amazon Cognito, Amazon DynamoDB, and Amazon Elastic Transcoder.
The interns should be able to create and configure the necessary resources, but they may not have access to create or modify AWS IAM roles. The Solutions
Architect creates a policy and attaches it to the interns' group.
How should the Security team configure the environment to ensure that the interns are self-sufficient?
A
A company is running a commercial Apache Hadoop cluster on Amazon EC2. This cluster is being used daily to query large files on Amazon S3. The data on
Amazon S3 has been curated and does not require any additional transformations steps. The company is using a commercial business intelligence (BI) tool on
Amazon EC2 to run queries against the Hadoop cluster and visualize the data.
The company wants to reduce or eliminate the overhead costs associated with managing the Hadoop cluster and the BI tool. The company would like to move to a more cost-effective solution with minimal effort. The visualization is simple and requires performing some basic aggregation steps only.
Which option will meet the company's requirements?
C
Reference:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/quicksight/latest/user/create-a-data-set-athena.html https://aws.amazon.com/athena/
A large multinational company runs a timesheet application on AWS that is used by staff across the world. The application runs on Amazon EC2 instances in an
Auto Scaling group behind an Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) load balancer, and stores data in an Amazon RDS MySQL Multi-AZ database instance.
The CFO is concerned about the impact on the business if the application is not available. The application must not be down for more than two hours, but he solution must be as cost-effective as possible.
How should the Solutions Architect meet the CFO's requirements while minimizing data loss?
C
A Development team has created a series of AWS CloudFormation templates to help deploy services. They created a template for a network/virtual private cloud
(VPC) stack, a database stack, a bastion host stack, and a web application-specific stack. Each service requires the deployment of at least:
✑ A network/VPC stack
✑ A bastion host stack
✑ A web application stack
Each template has multiple input parameters that make it difficult to deploy the services individually from the AWS CloudFormation console. The input parameters from one stack are typically outputs from other stacks. For example, the VPC ID, subnet IDs, and security groups from the network stack may need to be used in the application stack or database stack.
Which actions will help reduce both the operational burden and the number of parameters passed into a service deployment? (Choose two.)
AE
Your department creates regular analytics reports from your company's log files All log data is collected in Amazon S3 and processed by daily Amazon Elastic
MapReduce (EMR) jobs that generate daily PDF reports and aggregated tables in CSV format for an Amazon Redshift data warehouse.
Your CFO requests that you optimize the cost structure for this system.
Which of the following alternatives will lower costs without compromising average performance of the system or data integrity for the raw data?
C
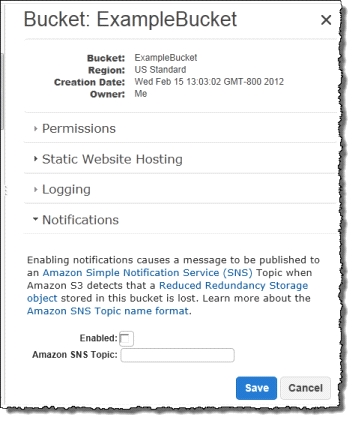
Using Reduced Redundancy Storage Amazon S3 stores objects according to their storage class. It assigns the storage class to an object when it is written to
Amazon S3. You can assign objects a specific storage class (standard or reduced redundancy) only when you write the objects to an Amazon S3 bucket or when you copy objects that are already stored in Amazon S3. Standard is the default storage class. For information about storage classes, see
Object Key and -
Metadata -
.
In order to reduce storage costs, you can use reduced redundancy storage for noncritical, reproducible data at lower levels of redundancy than Amazon S3 provides with standard storage. The lower level of redundancy results in less durability and availability, but in many cases, the lower costs can make reduced redundancy storage an acceptable storage solution. For example, it can be a cost-effective solution for sharing media content that is durably stored elsewhere. It can also make sense if you are storing thumbnails and other resized images that can be easily reproduced from an original image.
Reduced redundancy storage is designed to provide 99.99% durability of objects over a given year. This durability level corresponds to an average annual expected loss of 0.01% of objects. For example, if you store 10,000 objects using the RRS option, you can, on average, expect to incur an annual loss of a single object per year (0.01% of 10,000 objects).
Note:
This annual loss represents an expected average and does not guarantee the loss of less than 0.01% of objects in a given year.
Reduced redundancy storage stores objects on multiple devices across multiple facilities, providing 400 times the durability of a typical disk drive, but it does not replicate objects as many times as Amazon S3 standard storage. In addition, reduced redundancy storage is designed to sustain the loss of data in a single facility.
If an object in reduced redundancy storage has been lost, Amazon S3 will return a 405 error on requests made to that object. Amazon S3 also offers notifications for reduced redundancy storage object loss: you can configure your bucket so that when Amazon S3 detects the loss of an RRS object, a notification will be sent through Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS). You can then replace the lost object. To enable notifications, you can use the Amazon S3 console to set the Notifications property of your bucket.