A company's web application uses an Amazon RDS PostgreSQL DB instance to store its application data. During the financial closing period at the start of every month, Accountants run large queries that impact the database's performance due to high usage. The company wants to minimize the impact that the reporting activity has on the web application.
What should a solutions architect do to reduce the impact on the database with the LEAST amount of effort?
A
Amazon RDS uses the MariaDB, MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, and Microsoft SQL Server DB engines' built-in replication functionality to create a special type of
DB instance called a read replica from a source DB instance. Updates made to the source DB instance are asynchronously copied to the read replica. You can reduce the load on your source DB instance by routing read queries from your applications to the read replica.
When you create a read replica, you first specify an existing DB instance as the source. Then Amazon RDS takes a snapshot of the source instance and creates a read-only instance from the snapshot. Amazon RDS then uses the asynchronous replication method for the DB engine to update the read replica whenever there is a change to the source DB instance. The read replica operates as a DB instance that allows only read-only connections. Applications connect to a read replica the same way they do to any DB instance. Amazon RDS replicates all databases in the source DB instance.
Reference:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonRDS/latest/UserGuide/USER_ReadRepl.html
A company wants to migrate a high performance computing (HPC) application and data from on-premises to the AWS Cloud. The company uses tiered storage on premises with hot high-performance parallel storage to support the application during periodic runs of the application, and more economical cold storage to hold the data when the application is not actively running.
Which combination of solutions should a solutions architect recommend to support the storage needs of the application? (Choose two.)
AD
A company's application is running on Amazon EC2 instances in a single Region. In the event of a disaster, a solutions architect needs to ensure that the resources can also be deployed to a second Region.
Which combination of actions should the solutions architect take to accomplish this? (Choose two.)
BD
Cross Region EC2 AMI Copy -
We know that you want to build applications that span AWS Regions and we're working to provide you with the services and features needed to do so. We started out by launching the EBS Snapshot Copy feature late last year. This feature gave you the ability to copy a snapshot from Region to Region with just a couple of clicks. In addition, last month we made a significant reduction (26% to 83%) in the cost of transferring data between AWS Regions, making it less expensive to operate in more than one AWS region.
Today we are introducing a new feature: Amazon Machine Image (AMI) Copy. AMI Copy enables you to easily copy your Amazon Machine Images between AWS
Regions. AMI Copy helps enable several key scenarios including:
Simple and Consistent Multi-Region Deployment ג€" You can copy an AMI from one region to another, enabling you to easily launch consistent instances based on the same AMI into different regions.
Scalability ג€" You can more easily design and build world-scale applications that meet the needs of your users, regardless of their location.
Performance ג€" You can increase performance by distributing your application and locating critical components of your application in closer proximity to your users.
You can also take advantage of region-specific features such as instance types or other AWS services.
Even Higher Availability ג€" You can design and deploy applications across AWS regions, to increase availability.
Once the new AMI is in an Available state the copy is complete.
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/ec2-ami-copy-between-regions/
A solutions architect needs to ensure that API calls to Amazon DynamoDB from Amazon EC2 instances in a VPC do not traverse the internet.
What should the solutions architect do to accomplish this? (Choose two.)
AB
A VPC endpoint enables you to privately connect your VPC to supported AWS services and VPC endpoint services powered by AWS PrivateLink without requiring an internet gateway, NAT device, VPN connection, or AWS Direct Connect connection. Instances in your VPC do not require public IP addresses to communicate with resources in the service. Traffic between your VPC and the other service does not leave the Amazon network.
Gateway endpoints -
A gateway endpoint is a gateway that you specify as a target for a route in your route table for traffic destined to a supported AWS service. The following AWS services are supported:
Amazon S3 -
DynamoDB -
Reference:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/vpc-endpoints.html
A company's legacy application is currently relying on a single-instance Amazon RDS MySQL database without encryption. Due to new compliance requirements, all existing and new data in this database must be encrypted.
How should this be accomplished?
C
How do I encrypt Amazon RDS snapshots?
The following steps are applicable to Amazon RDS for MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, PostgreSQL, or MariaDB.
Important: If you use Amazon Aurora, you can restore an unencrypted Aurora DB cluster snapshot to an encrypted Aurora DB cluster if you specify an AWS Key
Management Service (AWS KMS) encryption key when you restore from the unencrypted DB cluster snapshot. For more information, see Limitations of Amazon
RDS Encrypted DB Instances.
Open the Amazon RDS console, and then choose Snapshots from the navigation pane.
Select the snapshot that you want to encrypt.
Under Snapshot Actions, choose Copy Snapshot.
Choose your Destination Region, and then enter your New DB Snapshot Identifier.
Change Enable Encryption to Yes.
Select your Master Key from the list, and then choose Copy Snapshot.
After the snapshot status is available, the Encrypted field will be True to indicate that the snapshot is encrypted.
You now have an encrypted snapshot of your DB. You can use this encrypted DB snapshot to restore the DB instance from the DB snapshot.
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/encrypt-rds-snapshots/
A manufacturing company wants to implement predictive maintenance on its machinery equipment. The company will install thousands of IoT sensors that will send data to AWS in real time. A solutions architect is tasked with implementing a solution that will receive events in an ordered manner for each machinery asset and ensure that data is saved for further processing at a later time.
Which solution would be MOST efficient?
D
A company's website runs on Amazon EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer (ALB). The website has a mix of dynamic and static content. Users around the globe are reporting that the website is slow.
Which set of actions will improve website performance for users worldwide?
A
What Is Amazon CloudFront?
Amazon CloudFront is a web service that speeds up distribution of your static and dynamic web content, such as .html, .css, .js, and image files, to your users.
CloudFront delivers your content through a worldwide network of data centers called edge locations. When a user requests content that you're serving with
CloudFront, the user is routed to the edge location that provides the lowest latency (time delay), so that content is delivered with the best possible performance.
Routing traffic to an Amazon CloudFront web distribution by using your domain name.
If you want to speed up delivery of your web content, you can use Amazon CloudFront, the AWS content delivery network (CDN). CloudFront can deliver your entire website ג€" including dynamic, static, streaming, and interactive content ג€" by using a global network of edge locations. Requests for your content are automatically routed to the edge location that gives your users the lowest latency.
To use CloudFront to distribute your content, you create a web distribution and specify settings such as the Amazon S3 bucket or HTTP server that you want
CloudFront to get your content from, whether you want only selected users to have access to your content, and whether you want to require users to use HTTPS.
When you create a web distribution, CloudFront assigns a domain name to the distribution, such asd111111abcdef8.cloudfront.net. You can use this domain name in the URLs for your content, for example:
[1]
Alternatively, you might prefer to use your own domain name in URLs, for example:
[1]
If you want to use your own domain name, use Amazon Route 53 to create an alias record that points to your CloudFront distribution. An alias record is a Route
53 extension to DNS. It's similar to a CNAME record, but you can create an alias record both for the root domain, such as example.com, and for subdomains, such aswww.example.com. (You can create CNAME records only for subdomains.) When Route 53 receives a DNS query that matches the name and type of an alias record, Route 53 responds with the domain name that is associated with your distribution.
Reference:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/Route53/latest/DeveloperGuide/routing-to-cloudfront-distribution.html https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonCloudFront/latest/DeveloperGuide/Introduction.html
A company has been storing analytics data in an Amazon RDS instance for the past few years. The company asked a solutions architect to find a solution that allows users to access this data using an API. The expectation is that the application will experience periods of inactivity but could receive bursts of traffic within seconds.
Which solution should the solutions architect suggest?
C
AWS Lambda -
With Lambda, you can run code for virtually any type of application or backend service ג€" all with zero administration. Just upload your code and Lambda takes care of everything required to run and scale your code with high availability. You can set up your code to automatically trigger from other AWS services or call it directly from any web or mobile app.
How it works -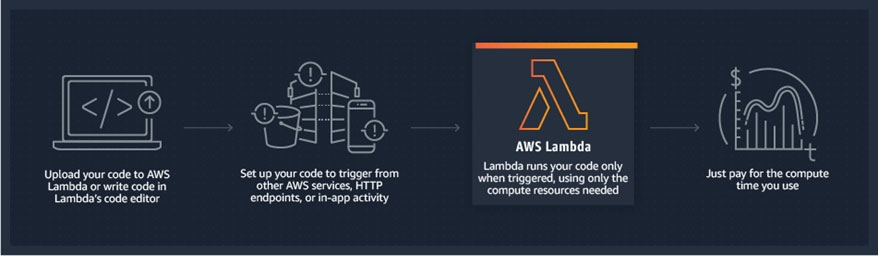
Amazon API Gateway -
Amazon API Gateway is a fully managed service that makes it easy for developers to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale. APIs act as the "front door" for applications to access data, business logic, or functionality from your backend services. Using API Gateway, you can create RESTful APIs and
WebSocket APIs that enable real-time two-way communication applications. API Gateway supports containerized and serverless workloads, as well as web applications.
API Gateway handles all the tasks involved in accepting and processing up to hundreds of thousands of concurrent API calls, including traffic management, CORS support, authorization and access control, throttling, monitoring, and API version management. API Gateway has no minimum fees or startup costs. You pay for the API calls you receive and the amount of data transferred out and, with the API Gateway tiered pricing model, you can reduce your cost as your API usage scales.
Reference:
https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/
https://aws.amazon.com/api-gateway/
A company must generate sales reports at the beginning of every month. The reporting process launches 20 Amazon EC2 instances on the first of the month. The process runs for 7 days and cannot be interrupted. The company wants to minimize costs.
Which pricing model should the company choose?
D
Explanation -
Scheduled Reserved Instances -
Scheduled Reserved Instances (Scheduled Instances) enable you to purchase capacity reservations that recur on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis, with a specified start time and duration, for a one-year term. You reserve the capacity in advance, so that you know it is available when you need it. You pay for the time that the instances are scheduled, even if you do not use them.
Scheduled Instances are a good choice for workloads that do not run continuously, but do run on a regular schedule. For example, you can use Scheduled
Instances for an application that runs during business hours or for batch processing that runs at the end of the week.
If you require a capacity reservation on a continuous basis, Reserved Instances might meet your needs and decrease costs.
How Scheduled Instances Work -
Amazon EC2 sets aside pools of EC2 instances in each Availability Zone for use as Scheduled Instances. Each pool supports a specific combination of instance type, operating system, and network.
To get started, you must search for an available schedule. You can search across multiple pools or a single pool. After you locate a suitable schedule, purchase it.
You must launch your Scheduled Instances during their scheduled time periods, using a launch configuration that matches the following attributes of the schedule that you purchased: instance type, Availability Zone, network, and platform. When you do so, Amazon EC2 launches EC2 instances on your behalf, based on the specified launch specification. Amazon EC2 must ensure that the EC2 instances have terminated by the end of the current scheduled time period so that the capacity is available for any other Scheduled Instances it is reserved for. Therefore, Amazon EC2 terminates the EC2 instances three minutes before the end of the current scheduled time period.
You can't stop or reboot Scheduled Instances, but you can terminate them manually as needed. If you terminate a Scheduled Instance before its current scheduled time period ends, you can launch it again after a few minutes. Otherwise, you must wait until the next scheduled time period.
The following diagram illustrates the lifecycle of a Scheduled Instance.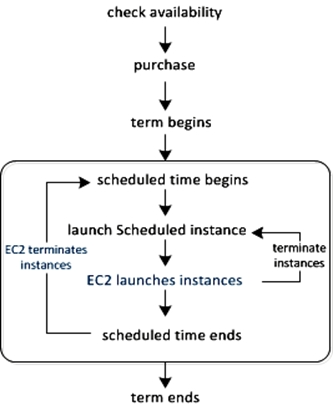
Reference:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/ec2-scheduled-instances.html
A gaming company has multiple Amazon EC2 instances in a single Availability Zone for its multiplayer game that communicates with users on Layer 4. The chief technology officer (CTO) wants to make the architecture highly available and cost-effective.
What should a solutions architect do to meet these requirements? (Choose two.)?
CE
Network Load Balancer overview -
A Network Load Balancer functions at the fourth layer of the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model. It can handle millions of requests per second. After the load balancer receives a connection request, it selects a target from the target group for the default rule. It attempts to open a TCP connection to the selected target on the port specified in the listener configuration.
When you enable an Availability Zone for the load balancer, Elastic Load Balancing creates a load balancer node in the Availability Zone. By default, each load balancer node distributes traffic across the registered targets in its Availability Zone only. If you enable cross-zone load balancing, each load balancer node distributes traffic across the registered targets in all enabled Availability Zones. For more information, see Availability Zones.
If you enable multiple Availability Zones for your load balancer and ensure that each target group has at least one target in each enabled Availability Zone, this increases the fault tolerance of your applications. For example, if one or more target groups does not have a healthy target in an Availability Zone, we remove the
IP address for the corresponding subnet from DNS, but the load balancer nodes in the other Availability Zones are still available to route traffic. If a client doesn't honor the time-to-live (TTL) and sends requests to the IP address after it is removed from DNS, the requests fail.
For TCP traffic, the load balancer selects a target using a flow hash algorithm based on the protocol, source IP address, source port, destination IP address, destination port, and TCP sequence number. The TCP connections from a client have different source ports and sequence numbers, and can be routed to different targets. Each individual TCP connection is routed to a single target for the life of the connection.
For UDP traffic, the load balancer selects a target using a flow hash algorithm based on the protocol, source IP address, source port, destination IP address, and destination port. A UDP flow has the same source and destination, so it is consistently routed to a single target throughout its lifetime. Different UDP flows have different source IP addresses and ports, so they can be routed to different targets.
An Auto Scaling group contains a collection of Amazon EC2 instances that are treated as a logical grouping for the purposes of automatic scaling and management. An Auto Scaling group also enables you to use Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling features such as health check replacements and scaling policies. Both maintaining the number of instances in an Auto Scaling group and automatic scaling are the core functionality of the Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling service.
The size of an Auto Scaling group depends on the number of instances that you set as the desired capacity. You can adjust its size to meet demand, either manually or by using automatic scaling.
An Auto Scaling group starts by launching enough instances to meet its desired capacity. It maintains this number of instances by performing periodic health checks on the instances in the group. The Auto Scaling group continues to maintain a fixed number of instances even if an instance becomes unhealthy. If an instance becomes unhealthy, the group terminates the unhealthy instance and launches another instance to replace it.
Reference:
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/elasticloadbalancing/latest/network/introduction.html https://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/ec2/userguide/AutoScalingGroup.html